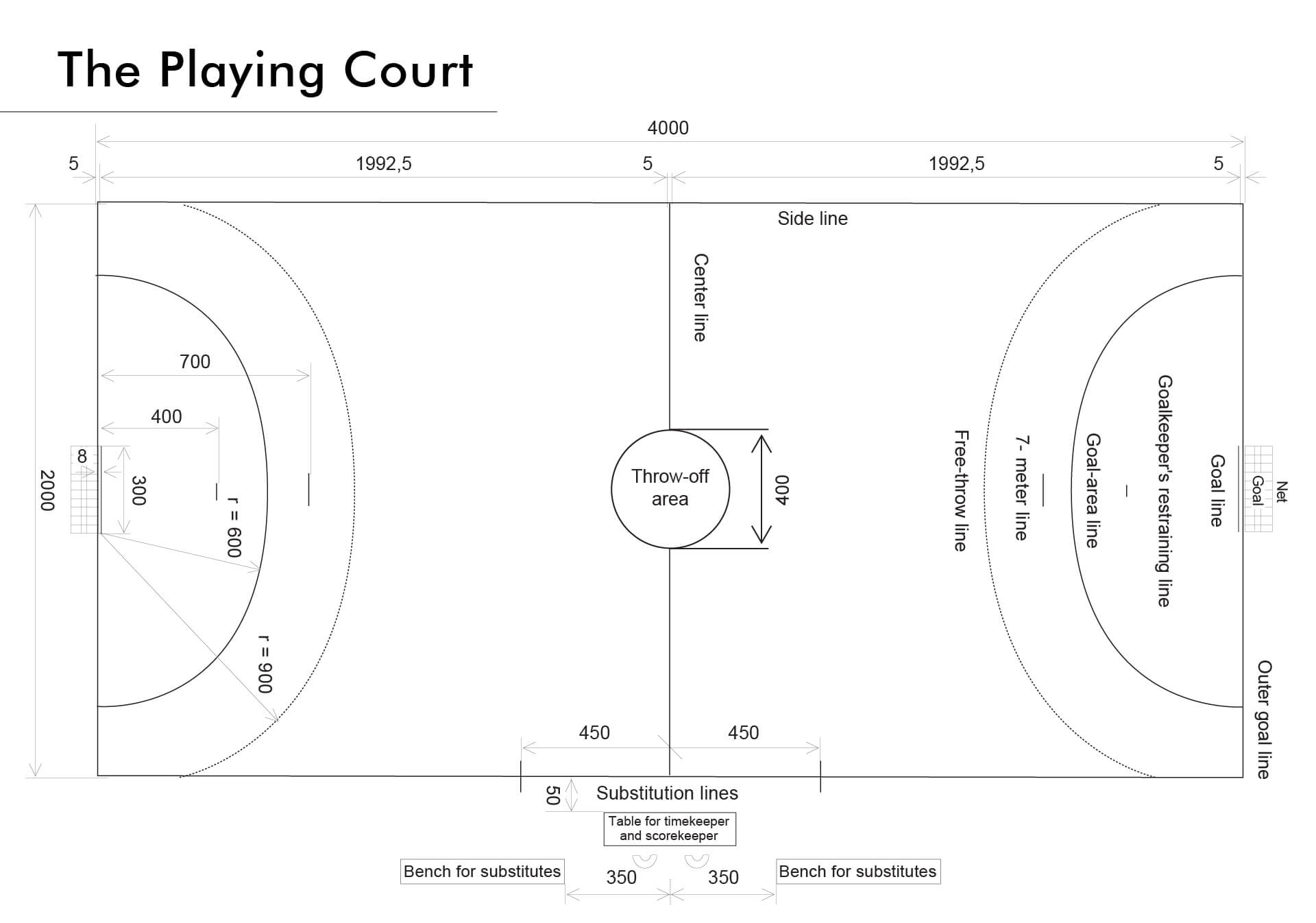
1:1 The playing court is a 40 meter long and 20 meter wide rectangle, consisting of two goal areas (see 1:4 and 6) and a playing area. The longer boundary lines are called side lines, and the shorter ones are called goal lines (between the goalposts) or outer goal lines (on either side of the goal).
There should be a safety zone surrounding the playing court, with a width of at least 1 meter along the side lines and 2 meters behind the goal lines.
The characteristics of the playing court must not be altered during the game in such a way that one team gains an advantage.
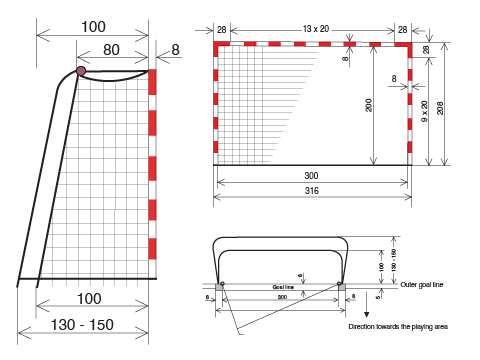
1:2 A goal is placed in the center of each outer goal line. The goals must be firmly attached to the floor or to the walls behind them. They have an interior height of 2 meters and a width of 3 meters.
The goalposts are joined by a horizontal crossbar. The rear side of the goalposts shall be in line with the rear edge of the goal line. The goalposts and the crossbar must have an 8cm square cross section. On the three sides which are visible from the court they must be painted in bands of two contrasting colors, which also contrast clearly with the background.
The goals must have a net, that should be attached in such a way that a ball thrown into the goal normally remains in the goal.
1:3 All lines on the court are fully part of the area that they enclose. The goal lines shall be 8cm wide between the goalposts (see diagram 2a), whereas all other lines shall be 5cm wide. Lines between two adjacent areas may be replaced with a difference in colors between the adjacent areas of the floor.
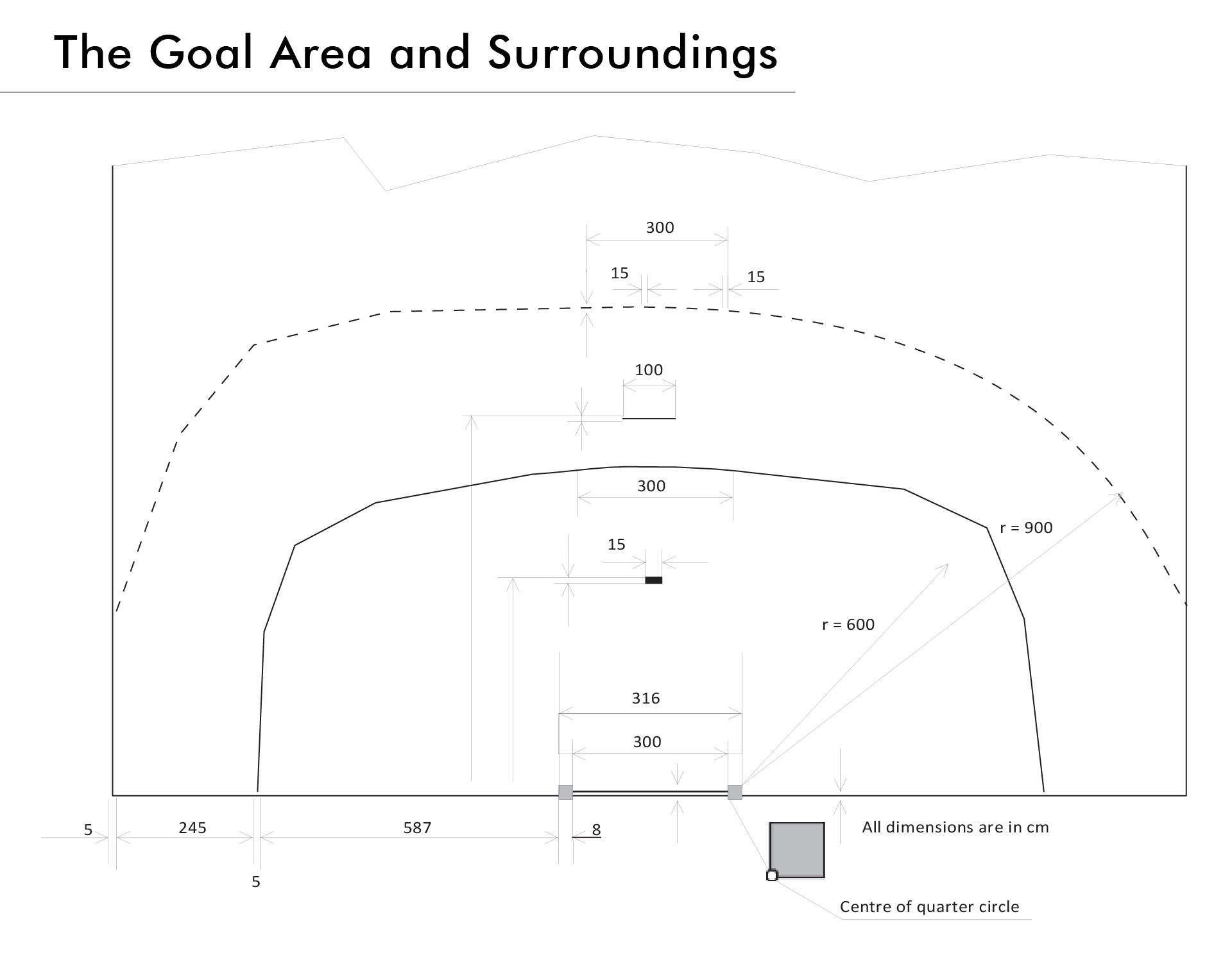
1:4 In front of each goal there is a goal area. The goal area is defined by the goal-area line (6-meter line), which is drawn as follows:
a) a 3 meter long line directly in front of the goal ; this line is parallel to the goal line and 6 meters away from it (measured from the rear edge of the goal line to the front edge of the goal-area line) ;
b) two quarter circles, each with a radius of 6 meters (measured from the rear inner corner of the goalposts), connecting the 3 meter long line with the outer goal.
1:5 The free throw line (9-meter line) is a broken line, drawn 3 meters outside the goal-area line. Both the segments of the line and the spaces between them measure 15cm.
1:6 The 7-meter line is a 1 meter long line, directly in front of the goal. It is parallel to the goal line and 7 meters away from it (measured from the rear edge of the goal line to the front edge of the 7-meter line).
1:7 The goalkeeper’s restraining line (the 4-meter line) is a 15cm long line, directly in front of the goal. It is parallel to the goal line and 4 meters away from it (measured from the rear edge of the goal line to the front edge of the 4-meter line).
1:8 The center line connects the midpoints of the two side lines.
1:9 A circle with a diameter of 4 meters, referred to as throw-off area, is placed in the middle of the center line. The throw-off area can be:
a) an area with a different color between the area and the playing court (diameter 4m).
b) a circle line.
1:10 The substitution line (a segment of the side line) for each team extends from the center line to a point at a distance of 4.5 meters from the center line. This end point of the substitution line is enhanced by a line which is parallel to the center line, extending 15cm inside the side line and 15cm outside the side line.
Note : More detailed technical requirements for the playing court and the goals can be found in the Guidelines for Playing Courts and Goals.
Dimensions of a goalpost and lateral view of a goalpost.
2:1 The normal playing time for all teams with players of age 16 and above is 2 halves of 30 minutes. The half-time break is normally 10 minutes.
2:2 Overtime is played, following a 5-minute break, if a game is tied at the end of the regular playing time and a winner has to be determined. The overtime period consists of 2 halves of 5 minutes, with a 1-minute half-time break.
If the game is again tied after a first overtime period, a second period is played after a 5-minute break. This overtime period also has 2 halves of 5 minutes, with a 1-minute half-time break.
If the game is still tied, the winner will be determined in accordance with the rules for the particular competition. In the case that the decision is to use 7-meter-throwing as tie-breaker to decide a winner, the procedures indicated below shall be followed.
Comments :
If 7-meter-throwing is used as a tie-breaker, players who are not suspended, disqualified or excluded at the end of the playing time are entitled to participate. Each team nominates 5 players. These players make one throw each, alternating with the players of the other team. The teams are not required to predetermine the sequence of their throwers. Goalkeepers may be freely chosen and substituted among the players eligible to participate. Players may participate in the 7-meter throwing as both throwers and goalkeepers.
The referees decide which goal is used. The referees make a coin toss, and the winning team chooses whether they wish to throw first or last. The opposite sequence is used for the remainder of the throws, if the throwing has to continue because the score is still tied after the first five throws each.
For such a continuation, each team shall again nominate five players. All or some of them may be the same as in the first round. This method of nominating five players at a time continues as long as it is necessary. However, the winner is now decided as soon as there is a goal difference after both teams have had the same number of throws.
Players may be disqualified from further participation in the 7-meter throwing in cases of significant or repeated unsportsmanlike conduct (16.6e). If this concerns a player who has just been nominated in a group of five throwers, the team must nominate another thrower.
2:3 The playing time begins with the referee’s whistle for the initial throw-off. It ends with the automatic final signal from the public clock or from the timekeeper. If no such signal comes, the referee whistles to indicate that the playing time is over (17:9).
Comment :
If a public clock with an automatic final signal is not available, the timekeeper shall use a table clock or a stopwatch and end the game with a final signal (18:2, 2nd paragraph).
2:4 Infractions and unsportsmanlike conduct that take place before or simultaneously with the final signal (for half-time or end of game, also in overtime) are to be punished, also if the resulting free-throw (under Rule 13:1) or 7-meter-throw cannot be taken until after the signal. Similarly, the throw must be retaken, if the final signal (for half-time or end of game, also in overtime) sounds precisely when a free-throw or a 7-meter throw is being executed or when the ball is already in the air.
In both cases, the referees end the game only after the free-throw or 7-meter throw has been taken (or retaken) and its immediate result has been established .
2:5 For free-throws taken (or retaken) under Rule 2:4, special restrictions apply regarding player positions and substitutions. As an exception to the normal substitution flexibility in Rule 4:4, the only player substitution allowed is for one player on the throwing team. Violations are penalized under Rule 4:5, 1st paragraph. Moreover, all the team mates of the thrower must be positioned at least 3 meters away from the thrower, in addition to being outside the free-throw line of the opponents (13:7, 15:6).
The positions of the defending players are indicated in Rule 13:8.
2:6 Players and team officials remain subject to personal punishment for infractions or unsportsmanlike conduct which take place during the execution of a free-throw or 7-meter throw in the circumstances described in Rules 2:4-5. An infraction during the execution of such a throw cannot, however, lead to a free-throw in the opposite direction.
2:7 If the referees determine that the timekeeper has given the final signal (for half-time or end of game, also in overtime) too early, they must keep the players on the court and play the remaining time.
The team that was in possession of the ball at the time of the premature signal will remain in possession when the game resumes. If the ball was out of play, then the game is restarted with the throw that corresponds to the situation. If the ball was in play, then the game is restarted with a free-throw in accordance with Rule 13:4a-b.
If the first half of a game (or an overtime period) has been terminated too late, the second half must be shortened correspondingly. If the second half of a game (or an overtime period) has been terminated too late, then the referees are no longer in a position to change anything.
2:8 The referees decide on the start and the duration of an interruption (“time-out”). A time-out is obligatory when:
a) a 2-minute suspension, disqualification, or exclusion is given ;
b) a team time-out is granted;
c) there is a whistle signal from the timekeeper or the technical delegate ;
d) consultations between the referees are necessary in accordance with Rule 17:7.
A time-out is normally also given in certain other situations, depending on the circumstances.
Infractions during a time-out have the same consequences as infractions during the playing time (16:10).
2:9 In principle, the referees decide when the clock is to be stopped and started in connection with a time-out. The interruption of the playing time is to be indicated to the timekeeper through three short blasts on the whistle and hand signal no. 15.
However, in the case of obligatory time-outs where the game has been interrupted by a whistle signal from the timekeeper or Delegate (2:8b-c), the timekeeper is required to stop the official clock immediately, without awaiting a confirmation from the referees.
The whistle must always be blown to indicate the restart of the game after a time-out (15:5b).
Comments :
A whistle signal from the timekeeper/ Delegate effectively stops the game. Even if the referees (and the players) do not immediately realize that the game has been stopped, any action on the court after whistle signal is invalid. This means that if a goal was scored after the whistle signal from the table, the ‘goal’ must be disallowed. Similarly, a decision to award a throw to a team (7-meter throw, free-throw, throw-in, throw-off or goalkeeper-throw) is also invalid. The game shall instead be restarted in the manner that corresponds to the situation that existed when the timekeeper/Delegate whistled. (It should be kept in mind that the typical reason for the intervention is a team time-out or a faulty substitution).
However, any personal punishment given by the referees between the time of the whistle from the table and the time the referees stop the action remains valid. This applies regardless of the type of the violation and regardless of the severity of the punishment.
2:10 Each team has the right to receive one 1-minute team time-out in each half of the regular playing time, but not in overtime.
Comments :
Each team has the right to receive three 1-minute team time-outs per match (overtime excluded) but may be granted a maximum of two team time-outs in each half of the regular playing time.
3:1 The ball is made of leather or a synthetic material. It must be spherical. The surface must not be shiny or slippery.
3:2 The following two different categories of handballs shall apply:
a) Handballs played with resin
The following ball sizes (i.e. circumference and weight) shall be used for the different age categories:
• 58 to 60 cm in circumference and 425 to 475 g in weight (IHF size 3) for men’s senior and men’s youth (aged 16 and older) players;
• 54 to 56 cm in circumference and 325 to 375 g in weight (IHF size 2) for women’s senior, women’s youth (aged 14 and older) and men’s youth (aged 12 to 16) players;
• 50 to 52 cm in circumference and 290 to 330 g in weight (IHF size 1) for women’s youth (aged 8 to 14) and men’s youth (aged 8 to 12) players.
b) Handballs played without resin
The following ball sizes (i.e. circumference and weight) shall be used for the different age categories:
• 55.5 to 57.5 cm in circumference and 400 to 425 g in weight (IHF size 3) for men’s senior and men’s youth (aged 16 and older) players;
• 51.5 to 53.5 cm in circumference and 300 to 325 g in weight (IHF size 2) for women’s senior, women’s youth (aged 14 and older) and men’s youth (aged 12 to 16) players;
• 49 to 51 cm in circumference and 290 to 315 g in weight (IHF size 1) for women’s youth (aged 8 to 14) and men’s youth (aged 8 to 12) players.
3:3 For every game there must be at least two balls available. The reserve balls must be immediately available at the timekeeper’s table during the game. The balls must meet the requirements of Rules 3:1-2.
3:4 The referees decide when to use a reserve ball. In such cases, the referees should get the reserve ball into play quickly in order to minimize interruptions and avoid time-outs.
4:1 A team consists of up to 14 players.
No more than 7 players may be present on the court at the same time. The remaining players are substitutes.
A player who is recognized as a goalkeeper may become a court player at any time (note, however, Rule 8:5 Comment, 2nd paragraph). Similarly, a court player may become a goalkeeper at any time (see, however, 4:4 and 4:7).
If a team is playing without a goalkeeper, a maximum number of 7 court players are allowed to be on the playing court at the same time (see Rules 4:7, 6:1, 6:2c, 6:3, 8:7f, 14:1a).
Rules 4:4-4:7 are to be applied to substitutions of a goalkeeper for a court player.
A team must have at least 5 players on the court at the start of the game.
The number of players on a team can be increased up to 14, at any time during the game, including overtime.
The game may continue even if a team is reduced to less than 5 players on the court. It is for the referees to judge whether and when the game should be permanently suspended (17:12).
4:2 A team is allowed to use a maximum of 4 team officials during the game. These team officials may not be replaced during the course of the game. One of them must be designated as the «responsible team official». Only this official is allowed to address the timekeeper/ scorekeeper and, possibly, the referees.
A team official is generally not allowed to enter the court during the game. A violation of this rule is to be penalized as unsportsmanlike conduct (see 8:7-10, 16:1b, 16:3e-g and 16:6c). The game is restarted with a free-throw for the opponents (13:1a-b).
The ‘responsible team official’ shall ensure that, once the game has started, no other persons than the (maximum 4) registered team officials and the players who are entitled to participate (see 4:3) are present in the substitution area. He is also responsible for the team’s compliance with the Substitution Area Regulations. Violations lead to progressive punishment for the ‘responsible team official’ (16:1b, 16:3e, and 16:6c).
4.3 A player or team official is entitled to participate if he is present at the start of the game and is included in the score sheet.
Players and team officials who arrive after the game has started must obtain their entitlement to participate from the timekeeper/ scorekeeper and must be entered into the score sheet.
A player who is entitled to participate may, in principle, enter the court through the team’s own substitution line at any time (see, however, 4:4 and 4:6).
The ‘responsible team official’ shall ensure that only players who are entitled to participate enter the court. A violation is to be penalized as unsportsmanlike conduct by the ‘responsible team official’ (13:1a-b, 16:1b. 16:3d, and 16:6c).
4.4 Substitutes may enter the court, at any time and repeatedly (see, however, Rule 2:5 and Rule 4:11), without notifying the timekeeper/scorekeeper, as long as the players they are replacing have already left the court (4:5).
The players involved in the substitution shall always leave and enter the court over their own team’s substitution line (4:5). These requirements also apply to the substitution of goalkeepers (see also 4:7 and 14:10).
The substitution rules also apply during a time-out (except during a team time-out).
Comments :
The purpose of the concept of the ‘substitution line’ is to ensure fair and orderly substitutions. It is not intended to cause punishments in other situations, where a player steps over the sideline or outer goal line in a harmless manner and without any intention of gaining an advantage (e.g., getting water or a towel at the bench just beyond the substitution line, or leaving the court in a sportsmanlike manner when receiving a suspension and crossing the sideline at the bench but just outside the 15cm line). Tactical and illegal usage of the area outside the court is dealt with separately in Rule 7:10.
4:5 A faulty substitution shall be penalized with a 2-minute suspension for the guilty player. If more than one player from the same team is guilty of faulty substitution in the same situation, only the first player committing an infraction is to be penalized.
The game is restarted with a free- throw for the opponents (13:1a-b).
4:6 If an additional player enters the court without a substitution, or if a player illegally interferes with the game from the substitution area, there shall be a 2-minute suspension for the player. Thus, the team must be reduced by one player on the court for the next 2 minutes (apart from the fact that the entering additional player must leave the court).
If a player enters the court while serving a 2-minute suspension, he shall be given an additional 2-minute suspension. This suspension shall begin immediately, so the team must be further reduced on the court during the overlap between the first and the second suspension.
The game is in both cases restarted with a free-throw for the opponents (13:1a-b).
4:7 All the court players on a team must wear identical uniforms. The combinations of colors and design for the two teams must be clearly distinguishable from each other. All players used in the goalkeeper position on a team must wear the same color, a color that distinguishes them from the court players of both teams and the goalkeeper(s) of the opposing team (17:3).
4:8 The players must wear numbers that are at least 20 cm high in the back of the shirt and at least 10cm in the front. The numbers used should be from 1 to 20. A player who is switching between the court player and goalkeeper positions must wear the same number in both positions. The color of the numbers must contrast clearly with the colors and design of the shirt.
4:9 The players must wear sports shoes.
It is not permitted to wear objects that could be dangerous to the players. This includes, for instance, head protection, face masks, bracelets, watches, rings, visible piercing, necklaces or chains, earrings, glasses without restraining bands or with solid frames, or any other objects which could be dangerous (17:3). Players who do not meet this requirement will not be allowed to take part until they have corrected the problem. Flat rings, small earrings and visible piercing may be allowed, as long as they are taped over in such a way that they are no longer deemed dangerous to other players. Headbands, head scarves and captains’ armlets are allowed, as long as they are made of soft, elastic material.
Players who do not meet this requirement will not be allowed to take part until they have corrected the problem.
The responsible team official confirms by signing the match report / player registration before the game has been started that all players are correctly equipped. If the referees observe faulty equipment after the game has been started (according to Rule 4:9), the responsible team official is to be punished progressively and the player concerned has to leave the playing court until he has corrected the problem.
If the team has any doubt about the equipment, the responsible team official has to contact the referees or the delegate before the start of the game.
4:10 A player who is bleeding or has blood on the body or uniform must leave the court immediately and voluntarily (through a normal substitution), in order to have the bleeding stopped, the wound covered, and the body and uniform cleaned off. The player must not return to the court until this has been done.
A player who does not follow the instructions of the referees in connection with this provision is deemed guilty of unsportsmanlike conduct (8:7, 16:1b and 16:3d).
4:11 In the case of an injury, the referees may give permission (through hand signals no. 15 and 16) for two of the persons who are entitled to participate (see 4:3) to enter the court during a time-out, for the specific purpose of assisting an injured player from their team.
After receiving medical care on the playing court, the player has to leave the court immediately. He can only re-enter the court following the third attack of his team.
Regardless of the counted number of attacks, the player can re-enter the playing court when the game is continued after the end of a half-time. If the player enters the playing court too early, he shall be punished according to Rule 4:4-4:6.
If additional persons enter the court after two persons have already entered, it shall be punished as illegal entry, in the case of a player under Rule 4:6 and 16:3a, and in the case of a team official under Rules 4:2, 16:1b, 16:3d and 16:6c. A person who has been permitted to enter the court but, instead of assisting the injured player, gives instructions to players, approaches opponents or referees etc., shall be considered guilty of unsportsmanlike conduct (16:1b, 16:3d and 16:6c).
The goalkeeper is allowed to :
5:1 touch the ball with any part of his body while in the act of defense inside the goal area;
5:2 move with the ball inside the goal area, without being subject to the restrictions applying to court players (7:2-4, 7:7); the goalkeeper is not allowed, however, to delay the execution of the goalkeeper- throw (6:4-5, 12:2 and 15:5b);
5:3 leave the goal area without the ball and participate in the game in the playing area; when doing so, the goalkeeper becomes subject to the rules applying to players in the playing area (except in the situation described in Rule 8:5 Comment, 2nd paragraph). The goalkeeper is considered to have left the goal area as soon as any part of the body touches the floor outside the goal-area line.
5:4 to leave the goal area with the ball and play it again in the playing area if he has not managed to control it.
The goalkeeper is not allowed to :
5:5 endanger the opponent while in the act of defense (8:3, 8:5, 8:5 Comment, 13:1b);
5:6 leave the goal area with the ball under control; this leads to a free-throw (according to 6:1, 13:1a and 15:7, 3rd paragraph), if the referees had whistled for the execution of the goalkeeper-throw; otherwise the goalkeeper-throw is simply repeated (15:7, 2nd paragraph); see, however, the advantage interpretation in 15:7, if the goalkeeper were to lose the ball outside the goal area after having crossed the line with the ball in his hand);
5:7 touch the ball when it is stationary or rolling on the floor outside the goal area, while he is inside the goal area (6:1, 13:1a);
5:8 take the ball into the goal area when it is stationary or rolling on the floor outside the goal area (6:1, 13:1a);
5:9 re-enter the goal area from the playing area with the ball (6:1, 13:1a);
5:10 touch the ball with the foot or the leg below the knee, when it is stationary on the floor in the goal area or moving out towards the playing area (13:1a);
5:11 cross the goalkeeper’s restraining line (4-meter line) or its projection on either side, before the ball has left the hand of the opponent who is executing a 7-meter throw (14:9).
Comment :
As long as the goalkeeper keeps one foot on the floor on or behind the restraining line (4-meter line), he is permitted to move the other foot or any other part of his body out over the line in the air.
6:1 Only the goalkeeper is allowed to enter the goal area (see, however, 6:3). The goal area, which includes the goal-area line, is considered entered when a court player touches it with any part of the body.
6:2 When a court player enters the goal area, the decisions shall be as follows :
a) goalkeeper-throw when a player of the team in possession enters the goal area in possession of the ball or enters without the ball but gains an advantage by doing so (12:1);
b) free throw when a court player of the defending team enters the goal area and gains an advantage, but without destroying a chance of scoring (13:1b; see also 8:7f);
c) 7-meter throw when a court player of the defending team enters the goal area and because of this destroys a clear chance of scoring (14:1a). For purposes of this rule, the concept “entering the goal area” does not mean just touching the goal-area line, but clearly stepping into the goal area.
6:3 Entering the goal area is not penalized when:
a) a player enters the goal area after playing the ball, as long as this does not create a disadvantage for the opponents;
b) a player from one of the teams enters the goal area without the ball and does not gain an advantage by doing so;
6:4 The ball is considered to be ‘out of play’ when the goalkeeper controls the ball with his hands in the goal area (12:1). The ball must be put back into play through a goalkeeper-throw (12:2).
6:5 The ball remains in play, while it is rolling on the floor inside the goal area. It is in the possession of the goalkeeper’s team an only the goalkeeper may touch it. The goalkeeper may pick it up, which brings it out of play, and then put it back into play, in accordance with 6:4 and 12:1-2 (see, however, 6:7b). It leads to a free-throw (13:1a) if the ball is touched by a teammate of the goalkeeper while it is rolling (see, however, 14:1a), and the game is continued with a goalkeeper-throw (12:1 (iii)) if it is touched by an opponent.
The ball is out of play, as soon as it is lying on the floor in goal area (12:1 (ii)). It is in the possession of the goalkeeper’s team and only the goalkeeper may touch it. The goalkeeper must put it back into play in accordance with 6:4 and 12:2 (see, however, 6:7b). It remains a goalkeeper-throw if the ball is touched by any other player of either team (12:1 2nd paragraph, 13:3).
It is permitted to touch the ball when it is in the air over the goal area, as long as it is in conformity with Rules 7:1 and 7:8.
6:6 Play shall continue (through a goalkeeper-throw according to 6:4-5) if a player of the defending team touches the ball when in the act of defense, and the ball is caught by the goalkeeper or comes to rest in the goal area.
6:7 If a player plays the ball into his own goal area, the decisions shall be as follows:
a) goal if the ball enters the goal;
b) free-throw if the ball comes to a rest in the goal area, or if the goalkeeper touches the ball and it does not enter the goal (13:1a-b);
c) throw-in if the ball goes out over the outer goal line (11:1);
d) play continues if the ball passes through the goal area back into the playing area, without being touched by the goalkeeper.
6:8 A ball that returns from the goal area out into the playing area remains in play.
It is permitted to :
7:1 throw, catch, stop, push or hit the ball, by using hands (open or closed), arms, head, torso, thighs, and knees;
7:2 hold the ball for a maximum of 3 seconds, also when it is Iying on the floor (13:1a);
7:3 take a maximum of 3 steps with the ball (13:1a); one step is considered taken when:
a) a player who is standing with both feet on the floor lifts one foot and puts it down again, or moves one foot from one place to another;
b) a player is touching the floor with one foot only, catches the ball and then touches the floor with the other foot;
c) a player after a jump touches the floor with one foot only, and then hops on the same foot or touches the floor with the other foot;
d) a player after a jump touches the floor with both feet simultaneously, and then lifts one foot and puts it down again, or moves one foot from one place to another.
Comment :
If one foot is moved from one place to another and the other foot is dragged behind, only one step is considered taken. It is in conformance with the rules, if a player with the ball falls to the floor, slides and then stands up and plays the ball. This is also the case, if a player dives for the ball, controls it and stands up to play it.
7:4 while standing or running:
a) bounce the ball once and catch it again with one or both hands;
b) bounce the ball repeatedly with one hand (dribble), and then catch it or pick it up again with one or both hands;
c) roll the ball on the floor repeatedly with one hand, and then catch it or pick it up again with one or both hands.
As soon as the ball thereafter is held in one or both hands, it must be played within 3 seconds or after no more than 3 steps (13:1a).
The bouncing or dribbling is considered to have started when the player touches the ball with any part of his body and directs it towards the floor.
After the ball has touched another player or the goal, the player is allowed to tap the ball or bounce it and catch it again (see, however, 14:6).
7:5 move the ball from one hand into the other one;
7:6 play the ball while kneeling, sitting or lying on the floor; this means that is it permitted to execute a throw (for instance a free-throw), from such a position, if the requirements of Rule 15:1 are met, including the requirement of having a part of one foot in constant contact with the floor.
It is not permitted to :
7:7 after the ball has been controlled, to touch it more than once, unless it has touched the floor, another player, or the goal in the meantime (13:1a); however, touching it more than once is not penalized, if the player is ‘fumbling’ the ball, i.e., failing to control it when trying to catch or stop it;
7:8 touch the ball with a foot or leg below the knee, except when the ball has been thrown at the player by an opponent (13:1a-b; see also 8:7e);
7:9 Play continues if the ball touches a referee on the court.
7:10 If a player with the ball moves outside the playing court with one or both feet (while the ball is still inside the court), for instance to get around a defending player, this shall lead to a free-throw for the opponents (13:1a).
If a player from the team in possession takes up position outside the court without the ball, the referees shall indicate to the player that he must move into the court. If the player does not do so, or if the action is later repeated by the same team, there shall be a free-throw awarded to the opponents (13:1a) without any further forewarning. Such actions shall not lead to personal punishment under Rules 8 and 16.
7:11 It is not permitted to keep the ball in the team’s possession without making any recognizable attempt to attack or to shoot on goal. Similarly, it is not allowed to delay repeatedly the execution of a throw-off, free-throw, throw-in, or goalkeeper-throw for one’s own team. This is regarded as passive play, which is to be penalized with a free-throw against the team in possession of the ball unless the passive tendency ceases (13:1a).
The free-throw is taken from the spot where the ball was when play was interrupted.
7:12 When a tendency to passive play is recognized, the forewarning signal (hand signal no. 17) is shown. This gives the team in possession of the ball the opportunity to change its way of attacking in order to avoid losing possession. If the way of attacking does not change after the forewarning signal has been shown, the referees can whistle for passive play at any moment. If no shot on goal is taken by the attacking team after a maximum of 4 passes, then a free throw is called against this team (13:1a, procedure and exceptions see Clarification No. 4, section D).
The decision by the referees about the number of passes is a decision on the basis of their observation of facts under the principle of Rule 17:11.
In certain situations the referees can call a free throw against the team in possession also without any prior forewarning signal, e.g. when a player intentionally refrains from trying to utilize a clear scoring chance.
It is permitted:
8:1
a) to use an open hand to play the ball out of the hand of another player.
b) to use bent arms to make body contact with an opponent, and to monitor and follow him in this way.
c) to use one’s trunk to block the opponent, in a struggle for positions.
Comment:
Blocking means preventing an opponent from moving into open space. Setting the block, maintaining the block and moving out of the block must, in principle, be done in a passive manner in relation to the opponent (see, however, 8:2b).
It is not permitted:
8:2
a) to pull or hit the ball out of the hands of an opponent.
b) to block the opponent with arms, hand, legs, or to use any part of the body to displace him or push him away; this includes a dangerous use of the elbow, both as a starting position and in motion.
c) to hold an opponent (body or uniform), even if he remains free to continue the play.
d) to run into or jump into an opponent.
8:3 Fouls, where the action is mainly or exclusively aimed at the body of the opponent, must lead to a personal punishment. This means that, in addition to a free throw or 7-metre throw, at least the foul is to be punished progressively, beginning with a warning (16:1), then with 2-minute suspensions (16:3b) and disqualification (16:6d).
For more severe fouls, there are 3 further levels of punishment on the basis of the following decision-making criteria:
• Fouls that are to be punished with an immediate 2-minute suspension (8:4);
• Fouls that are to be punished with a disqualification (8:5);
• Fouls that are to be punished with a disqualification and where a written report is required (8:6).
For the judgment as to which personal punishments are appropriate for specific fouls, the following decision-making criteria apply; these criteria are to be used in combination as appropriate in each situation:
a) the position of the player who commits the foul (frontal position, from the side, or from behind);
b) the part of the body against which the illegal action is aimed (torso, shooting arm, legs, head/throat/neck);
c) the dynamics of the illegal action (the intensity of the illegal body contact, and/or a foul where the opponent is in full motion);
d) the effect of the illegal action:
• the impact on the body and ball control
• the reduction or prevention of the ability to move
• the prevention of the continuation of the game
For the judgment of fouls the particular game situation is relevant, too (e.g., shooting action, running into open space, situations with high running speed).
8:4 For certain fouls, the punishment is a direct 2-minute suspension, regardless of whether the player had received a warning earlier. This applies especially for such fouls where the guilty player disregards the danger to the opponent (see also 8:5 and 8:6). Taking into account the decision-making criteria under 8:3, such fouls could for instance be:
a) fouls that are committed with high intensity or against an opponent who is running fast;
b) holding on to the opponent for a long time, or pulling him down;
c) fouls against the head, throat or neck;
d) hard hitting against the torso or throwing arm;
e) attempting to make the opponent lose body control (e.g., grabbing the leg/foot of an opponent who is jumping; see, however, 8:5a);
f) running or jumping with great speed into an opponent.
8:5 A player who is attacking an opponent in a way that is dangerous to his health is to be disqualified (16:6a). The special danger to the opponent’s health follows from the high intensity of the foul or from the fact that the opponent is completely unprepared for the foul and therefore cannot protect himself (see Rule 8:5 Comment). In addition to the criteria of 8:3 and 8:4, the following decision-making criteria also apply:
a) the actual loss of body control while running or jumping, or during a throwing action;
b) a particularly aggressive action against a part of the body of the opponent, especially face, throat or neck; (the intensity of the body contact);
c) the reckless attitude demonstrated by the guilty player when committing the foul.
Comment:
Also a foul with a very small physical impact can be very dangerous and lead to a severe injury, if the foul is committed in a moment when the player is jumping in the air or running, and therefore is unable to protect himself. In this type of situation, it is the danger to the opponent and not the intensity of the body contact that is the basis for the judgment whether a disqualification is warranted.
This also applies in those situations where a goalkeeper leaves the goal area, for the purpose of catching a pass intended for an opponent. Here the goalkeeper has the responsibility for ensuring that a situation does not arise that is dangerous to the health of the opponent.
He is to be disqualified if he:
a) gains possession of the ball, but in his movement causes a collision with the opponent;
b) cannot reach or control the ball, but causes a collision with the opponent.
If the referees are convinced in one of these situations, that, without the illegal action from the goalkeeper, the opponent would have been able to reach the ball, then a 7-metre throw is to be awarded.
8:6 If the referees find an action to be particularly reckless, particularly dangerous, premeditated or malicious, they must submit a written report after the game, so that the responsible authorities are in a position to take a decision about further measures. Indications and characteristics that could serve as decision-making criteria in addition to those in Rule 8:5 are:
a) a particularly reckless or particularly dangerous action;
b) a premeditated or malicious action, which is not in any way related to the game situation.
Comment:
When a foul under Rule 8:5 or 8:6 is committed during the last 30 seconds of a game, with the purpose of preventing a goal, then the action is to be seen as ‘extremely unsportsmanlike conduct’ under Rule 8:10d and punished accordingly.
As unsportsmanlike conduct is considered any verbal and non-verbal expressions that are not in conformity with the spirit of good sportsmanship. This applies to both players and team officials, on the court and outside the court. For the punishment of unsportsmanlike, seriously unsportsmanlike, and extremely unsportsmanlike conduct, a difference is made between 4 levels of actions:
• Actions that are to be punished progressively (8:7);
• Actions that are to be punished with a direct 2-minute suspension (8:8);
• Actions that are to be punished with a disqualification (8:9);
• Actions that are to be punished with a disqualification and a written report (8:10a,b).
8:7 The actions listed below under a-f are examples of unsportsmanlike conduct that is to be punished progressively, beginning with a warning (16:1b).
a) protests against referee decisions, or verbal and non-verbal actions intended to cause a specific referee decision;
b) harassing an opponent or teammate through words or gestures, or shouting at an opponent in order to cause distraction;
c) delaying the execution of a formal throw for the opponents, by not respecting the 3-metre distance or in some other way;
d) through ‘theatre’, trying to mislead the referees regarding the actions of an opponent or exaggerating the impact of an action, in order to provoke a time-out or an undeserved punishment for an opponent;
e) actively blocking a shot or pass by using a foot or lower leg; pure reflex motions, e.g., moving the legs together, are not to be punished (see also Rule 7:8);
f) repeated entering of the goal area for tactical reasons.
8:8 Certain unsportsmanlike actions are by their nature seen as more severe and warrant an immediate 2-minute suspension, regardless of whether the player or the officials had received a warning earlier. This includes:
a) protests involving loudness with forceful gestures, or provocative behavior;
b) when there is a decision against a team in possession, and the player with the ball does not immediately make it available to the opponents by dropping it or putting it down on the floor;
c) blocking the access to a ball that went into the substitution area;
d) when the shot of a player, who is unhindered and throwing in an open play situation, hits the goalkeeper’s head.
Comment:
Criteria for hitting the goalkeeper in the head with the ball:
• The rule is only applicable in open play situations, i.e. no defender is between the thrower and the goalkeeper.
• The head must be the first point of ball contact. The rule does not apply if the ball hits the goalkeeper’s head after hitting any other part of the goalkeeper’s body first.
• The rule does not apply if the goalkeeper is moving his head in the direction of the ball.
• If the goalkeeper tries to mislead the referees in order to provoke a punishment (for example after the ball hit the goalkeeper’s chest), the goalkeeper is to be punished according to Rule 8:7d.
8:9 Certain forms of unsportsmanlike conduct are considered so serious that they warrant a disqualification. The following are examples of such conduct:
a) throwing or hitting the ball away in a demonstrative manner, after a decision by the referees;
b) if a goalkeeper demonstratively refrains from trying to stop a 7-metre throw;
c) deliberately throwing the ball at an opponent during a stoppage in the game; if it is done with a lot of force and from very short distance, it is more appropriately regarded as a 'particularly reckless action’ under 8:6 above;
d) when a 7m shooter hits the goalkeeper’s head, if the goalkeeper is not moving his head in the direction of the ball;
e) when a free throw shooter hits a defender’s head, if the defender is not moving his head in the direction of the ball;
f) an act of revenge after having been fouled.
Comment:
In the case of a 7-metre throw or a free throw, the shooter has the responsibility not to endanger the goalkeeper or the defender.
8:10 If the referees classify a conduct as extremely unsportsmanlike, a punishment is granted according to the following regulations.
In cases involving the following infractions (a, b), serving as examples, the referees have to submit a written report after the game has been ended to allow the competent bodies to decide what measures shall be taken:
a) insulting or threatening behavior directed at another person, e.g., referee, timekeeper/scorekeeper, delegate, team official, player, spectator; the behavior may be in verbal or non-verbal form (e.g., facial expression, gestures, body language or body contact);
b) (I) the interference by a team official in the game, on the playing court or from the substitution area, or (II) a player destroying a clear chance of scoring, either through an illegal entry on the court (Rule 4:6) or from the substitution area.
In cases involving the following infractions (c, d), a 7m throw is awarded to the opponents.
c) if during the last 30 seconds of a game the ball is out of play, and a player or team official prevents or delays the execution of a throw for the opponents, in order to prevent them from being able to take a shot on goal or to obtain a clear scoring chance, the guilty player / official is to be disqualified and a 7m throw is to be granted to the opponents. It applies to any type of interference (e.g., with only limited physical action, interfering with the execution of a throw such as intercepting a pass, interference with the reception of the ball, not releasing the ball).
d) if during the last 30 seconds of a game the ball is in play, and the opponents (1) through an infringement by a player of the Rules 8:5 or 8:6 as well as 8:10a or 8:10b (II) (2) through an infringement by an official of the Rules 8:10a or 8:10b (I) prevent the team in possession from being able to take a shot on goal or to obtain a clear scoring chance, the guilty player or official is disqualified according to the corresponding Rules and the team in possession is granted a 7m throw.
If the player who was fouled, or a teammate, scores a goal before the game is interrupted, the 7m throw shall not be granted.
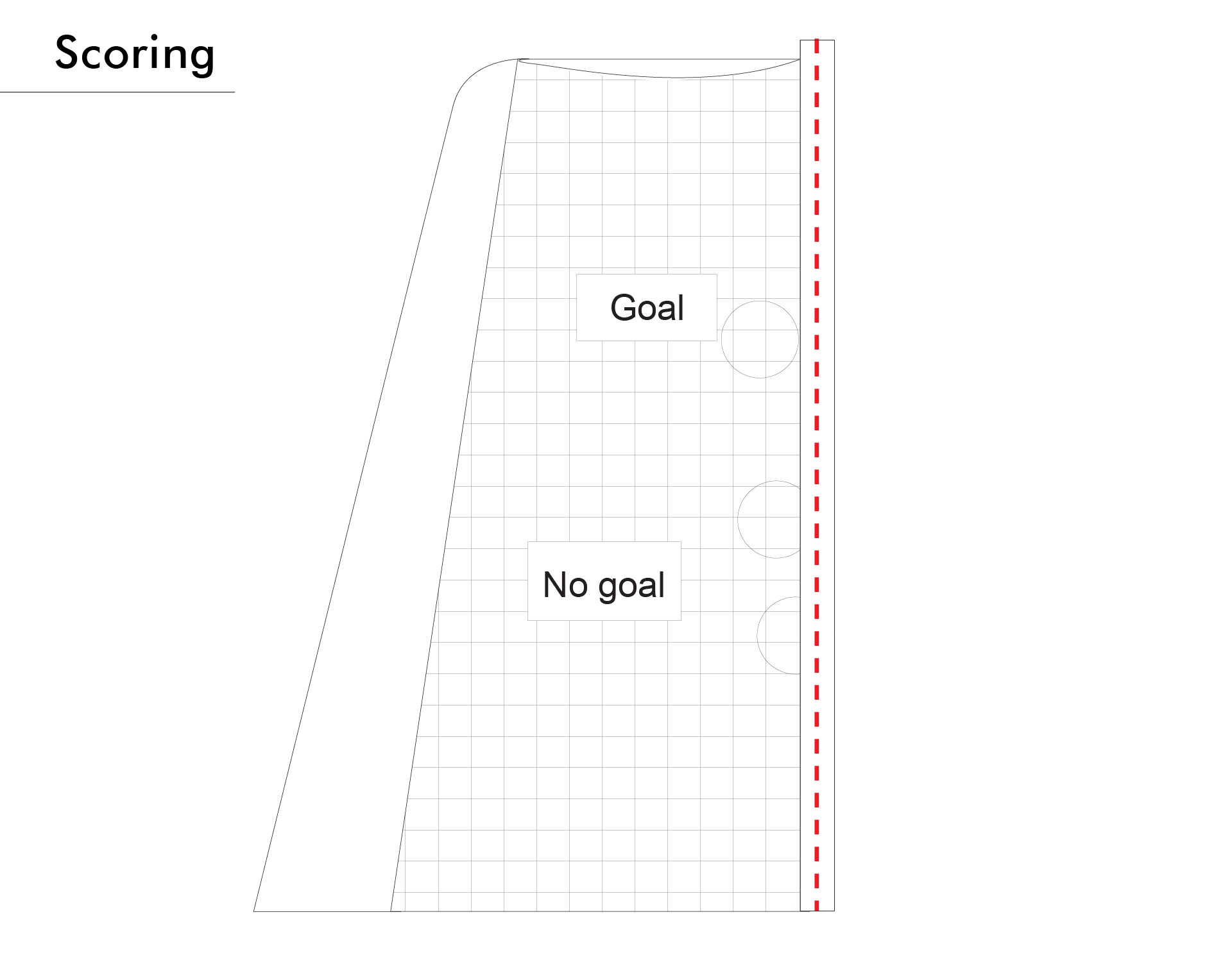
9:1 A goal is scored when the entire ball has completely crossed the goal line (see diagram), provided that no violation of the rules has been committed by the thrower, a teammate or a team official before or during the throw. The goal line referee confirms with two short whistle signals and hand signal no. 12 that a goal has been scored.
A goal shall be awarded if there is a violation of the rules by a defender but the ball still goes into the goal.
A goal cannot be awarded if a referee or the timekeeper has interrupted the game before the ball has completely crossed the goal line.
A goal shall be awarded to the opponents if a player plays the ball into his own goal, except in the situation where a goalkeeper is executing a goalkeeper-throw (12:2, 2nd paragraph).
Comment :
A goal shall be awarded if the ball is prevented from going into the goal by someone or something not participating in the game (spectators, etc.), and the referees are convinced that the ball would otherwise have entered the goal.
9:2 A goal that has been awarded can no longer be disallowed, once the referee has blown the whistle for the subsequent throw-off to be taken. (See, however, Rule 2:9 Comment).
The referees must make clear (without a throw-off) that they have awarded a goal, if the signal for the end of a half sounds immediately after a goal is scored and before a throw-off can be taken.
Comment :
A goal should be entered on the scoreboard as soon as it has been awarded by the referees.
9:3 The team that has scored more goals than the opponents is the winner. The game is tied if both teams have scored the same number of goals or no goals at all (see 2:2).
10:1 At the start of the game, the throw-off is taken by the team that wins the coin toss and elects to start with the ball in its possession. The opponents then have the right to choose ends. Alternatively, if the team that wins the coin toss prefers to choose ends, then the opponents take the throw-off.
The teams change ends for the second half of the game. The throw-off at the start of the second half is taken by the team that did not have the throw-off at the start of the game.
A new coin toss is undertaken prior to each overtime period, and all the above-stated regulations under Rule 10:1 also apply to overtime.
10:2 After a goal has been scored play is resumed with a throw-off taken by the team that conceded the goal (see, however, 9:2, 2nd paragraph).
10:3 The following two throw-off options shall apply:
a) Throw-off from the center line
The throw-off is taken in any direction from the center line (with a tolerance sideways of about 1.5 meters from the center of the court). It is preceded by a whistle signal, following which it must be taken within 3 seconds (13:1a, 15:7 3rd paragraph). The player taking the throw-off must take up a position with at least one foot on the center line, and the other foot on or behind the line (15:6), and remain in this position until the ball has left his hand (13:1a, 15:7 3rd paragraph) (see also Clarification No. 5). The teammates of the thrower are not allowed to cross the center line prior to the whistle signal (15:6).
b) Throw-off from the throw-off area
• The throw-off is taken in any direction from the throw-off area. It is preceded by a whistle signal, following which it must be taken within 3 seconds (13:1a, 15:7 3rd paragraph).
• The whistle signal by the referees can be given when the ball is inside the throw-off area and the thrower has at least one foot inside the throw-off area. (15:6).
• The thrower is not allowed to cross the throw-off area line with any part of the body until the throw-off is considered taken (13:1a, 15:7 3rd paragraph).
• The thrower is allowed to move inside the throw-off area, but he is not allowed to bounce the ball after the whistle signal (13:1a, 15:7 3rd paragraph).
• The execution can be done running. It is not allowed to jump during the execution of the throw-off (13:1a, 15:7 3rd paragraph).
• The throw-off is considered taken when either
• the ball has first left the hand of the thrower and then has completely crossed the throw-off area line; or
• the ball was passed and touched or controlled by a teammate, although it occurred inside the throw-off area.
• The teammates of the thrower are not allowed to cross the center line prior to the whistle signal, except if they are inside the throw-off area (15:6).
• The players of the defending team must be outside the throw-off area and are not allowed to touch the ball or the opponents inside the throw-off area until the throw is considered taken (15:4, 8:7c). They are allowed to be directly outside the throw-off area.
10:4 For the throw-off at the start of each half (incl. any period of overtime), all players must be in their own half of the court or inside the throw-off area, if applicable. However, for the throw-off after a goal has been scored, the opponents of the thrower are allowed to be in both halves of the court.
If the throw-off is taken from the center line (10:3a), the opponents must be at least 3 meters away from the player taking the throw-off (15:4, 15:9, 8:7c).
If the throw-off is taken from the throw-off area (10:3b), the opponents must be outside the area line with the entire body (15:4, 15:9, 8:7c).
11:1 A throw-in is awarded when the ball has completely crossed the side line, or when a court player on the defending team was the last one to touch the ball before it crossed his team’s outer goal line. It is also awarded when the ball has touched the ceiling or a fixture above the court.
11:2 The throw-in is taken without whistle signal from the referees (see, however, 15:5b) by the opponents of the team whose player last touched the ball before it crossed the line or touched the ceiling or fixture.
11:3 The throw-in is taken from the spot where the ball crossed the side line or, if it crossed the outer goal line, from the intersection of the side line and the outer goal line on that side. For a throw-in after the ball touched the ceiling or a fixture above the court, the throw-in is taken at the nearest point on the nearest side line in relation to the spot where the ball touched the ceiling or fixture.
11:4 The thrower must stand with a foot on the side line and remain in a correct position until the ball has left his hand. There is no limitation for the placement of the second foot (13:1a, 15:6, 15:7 2nd and 3rd paragraph).
11:5 While the throw-in is being taken, the opponents may not be closer than 3 meters to the thrower (15:4, 15:9, 8:7c).
They are, however, always allowed to stand immediately outside their goal-area line even if the distance between them and the thrower is less than 3 meters then.
12:1 A goalkeeper-throw is awarded when: (i) a player of the opposing team has entered the goal area in violation of Rule 6:2a; (ii) the goalkeeper has controlled the ball in the goal area or the ball is stationary on the floor in the goal area (6:4-5); (iii) a player of the opposing team has touched the ball when it is rolling or stationary on the floor in the goal area (6:5, 1st paragraph) or (iv) when the ball has crossed the outer goal line, after having been touched last by the goalkeeper or a player of the opposing team.
This means that in all these situations the ball is considered out of play, and that the game is resumed with a goalkeeper-throw (13:3) if there is a violation after a goalkeeper-throw has been awarded and before it has been executed.
12:2 The goalkeeper-throw is taken by the goalkeeper without whistle signal from the referee (see, however, 15:5b), from the goal area out over the goal area line.
If the team that has to execute the goalkeeper throw is playing without a goalkeeper, a goalkeeper must replace one of the court players (Rule 4:4). The referees decide if a time-out is necessary (Rule 2:8, 2nd paragraph, Clarification No. 2).
The goalkeeper-throw is considered to have been taken, when the ball thrown by the goalkeeper has completely crossed the goal-area line.
The players of the other team are allowed to be immediately outside the goal-area line, but they are not allowed to touch the ball until it has completely crossed the line (15:4, 15:9, 8:7c).
13:1 In principle, the referees interrupt the game and have it restarted with a free-throw for the opponents when:
a) the team in possession of the ball commits a violation of rules that must lead to a loss of possession (see 4:2-3, 4:5-6, 4:9, 5:6-10, 6:5 1st paragraph, 6:7b, 7:2-4, 7:7-8, 7:10, 7:11-12, 8:2-10, 10:3, 11:4, 13:7, 14:4-7, 15:7 3rd paragraph, and 15:8);
b) the opponents commit a violation of rules that causes the team in possession of the ball to lose it (see 4:2-3, 4:5-6, 5:5, 6:2b, 6:7b, 7:8, 8:2-10).
13:2 The referees should allow continuity in the game by refraining from interrupting the game prematurely with a free-throw decision.
This means that, under Rule 13:1a, the referees should not call a free-throw if the defending team gains possession of the ball immediately after the violation committed by the attacking team.
Similarly, under Rule 13:1b, the referees should not intervene until and unless it is clear that the attacking team has lost possession of the ball or is unable to continue their attack, due to the violation committed by the defending team.
If a personal punishment is to be given because of rules violation, then the referees may decide to interrupt the game immediately, if this does not cause a disadvantage for the opponents of the team committing the violation. Otherwise the punishment should be delayed until the existing situation is over.
Rule 13:2 does not apply in the case of infringements against Rules 4:2-3 or 4:5-6, where the game shall be interrupted immediately, normally through the intervention of the timekeeper, the delegate or the referees.
13:3 If a violation that would normally lead to a free throw under Rule 13:1a-b takes place when the ball is out of play, then the game is restarted with the throw that corresponds to the reason for the existing interruption (please see also Rules 8:10c, special instructions during the last 30 seconds of the game).
13:4 In addition to the situations indicated in Rule 13:1 a-b, a free-throw is also used as the way of restarting the game in certain situations where the game is interrupted (i.e. when the ball is in play), even though no violation of rules has occurred :
a) if one team is in possession of the ball at the time of the interruption, this team shall retain possession;
b)if neither team is in possession of the ball, then the team that last had possession shall be given possession again;
13:5 If there is a free-throw decision against the team that is in possession of the ball when the referee whistles, then the player who has the ball at that moment must immediately drop it or put it down on the floor, so that it can be played (8:8b).
13:6 The free-throw is normally taken without any whistle signal from the referee (see, however, 15:5b) and, in principle, from the place where the infraction occurred. The following are exceptions to this principle:
In the situations described under 13:4 a-b, the free-throw is taken, after whistle signal, in principle from the place where the ball was at the time of the interruption.
If a referee or technical delegate interrupts the game because of an infringement on the part of a player or team official of the defending team, and this results in a verbal caution or a personal punishment, then the free- throw should be taken from the place where the ball was when the game was interrupted, if this is a more favorable location than the position where the infringement took place.
The same exception as in the previous paragraph applies if a timekeeper interrupts the game because of violations under Rules 4:2-3 or 4:5-6.
As indicated in Rule 7:11, free-throws called because of passive play shall be taken from the place where the ball was when the game was interrupted.
Notwithstanding the basic principles and procedures stated in the preceding paragraphs, a free-throw can never be taken inside the throwing team’s own goal area or inside the free-throw line of the opponents. In any situation where the location indicated by the one of the preceding paragraphs involves either one of these areas, the location for the execution must be moved to the nearest spot immediately outside the restricted area.
Comments :
If the correct position for the free-throw is at the free-throw line of the defending team, then the execution must take place essentially at the precise spot. However, the further away the location is from the defending team’s free-throw line, the more of a margin there is for allowing the free-throw to be taken a short distance away from the precise spot. This margin gradually increases up to 3 meters, which applies in the case of a free-throw taken from just outside the throwing team’s own goal area.
The margin just explained does not apply following a violation of Rule 13:5, if this violation is being punished in accordance with Rule 8:8b. In such cases, the execution should always be from the precise spot where the violation has been committed.
13:7 Players of the throwing team must not touch or cross the free-throw line of the opponents before the free-throw has been taken. See also the special restriction under Rule 2:5.
The referees must correct the positions of players of the throwing team who are between the free-throw line and the goal-area line prior to the execution of the free-throw, if the incorrect positions have an influence on the game (15:3, 15:6). The free-throw shall then be taken following a whistle signal (15:5b). The same procedure applies (Rule 15:7, 2nd paragraph) if players of the throwing team enter the restricted area during the execution of the free-throw (before the ball has left the thrower’s hand), if the execution of the throw was not preceded by a whistle signal.
In the case where the execution of a free-throw has been authorized through a whistle signal, if players from the attacking team touch or cross the free-throw line before the ball has left the hand of the thrower, there shall be a free-throw awarded to the defending team (15:7, 3rd paragraph; 13:1a).
13:8 When a free throw is being taken, the opponents must remain at a distance of at least 3 meters from the thrower. They are, however, allowed to stand immediately outside their goal-area line if the free throw is being taken at their free throw line. Interference with the execution of the free throw is penalized in accordance with Rules 15:9 and 8:7c.
14:1 A 7-meter throw is awarded when:
a) a clear chance of scoring is illegally destroyed anywhere on the court by a player or a team official of the opposing team;
b) there is an unwarranted whistle signal at the time of a clear chance of scoring;
c) a clear chance of scoring is destroyed through the interference of someone not participating in the game, for instance a spectator entering the court or stopping the players through a whistle signal (except when 9:1 Comment applies).
d) there is an infraction according to Rules 8:10c or 8:10d (however, see 8:10 last paragraph).
By analogy, this rule also applies in the case of a ‘force majeure’, such as a sudden electrical failure, that stops the game precisely during a clear chance of scoring. See Clarification No. 6 for the definition of clear chance of scoring.
14:2 If an attacking player retains full control of ball and body despite a violation as in Rule 14:1a, there is no reason to give a 7-metre throw, even if thereafter the player fails to utilize the clear scoring chance.
Whenever there is a potential 7-meter decision, the referees should always hold off on intervening until they can clearly determine if a 7-meter decision is indeed justified and necessary. If the attacking player scores a goal despite the illegal interference from the defenders, then there is obviously no reason to give a 7-meter throw. Conversely, if it becomes apparent that the player really has lost ball or body control because of the violation, so that a clear chance no longer exists, then a 7-meter throw is to be given.
Rule 14:2 is not applicable in cases involving infractions of the Rules 4:2-3 or 4:5-6, when the game has to be interrupted immediately by a signal from the timekeeper, the delegate or the referees.
14:3 When awarding a 7-meter throw the referees may give a time-out, but only if there is a substantial delay, for instance due to a substitution of the goalkeeper or the thrower, and a time-out decision would be in line with the principles and criteria stated in Clarification No. 2.
14:4 The 7-meter throw is to be taken as a shot on goal, within 3 seconds after a whistle signal from the referee (15:7, 3rd paragraph; 13:1a).
14:5 The player who is taking the 7-meter throw must take up a position behind the 7-meter line, not further away than 1 meter behind the line (15:1, 15:6). After the whistle signal from the referee, the thrower must not touch or cross the 7-meter line before the ball has left his hand (15:7, 3rd paragraph; 13:1a).
14:6 The ball must not be played again by the thrower or a teammate following the execution of a 7-meter throw, until it has touched an opponent or the goal (15:7, 3rd paragraph; 13:1a).
14:7 When a 7-meter throw is being executed, the teammates of the thrower must position themselves outside the free-throw line, and remain there until the ball has left the thrower’s hand (15:3, 15:6). If they do not do so, a free-throw will be called against the team taking the 7-meter throw (15:7, 3rd paragraph; 13:1a).
14:8 When a 7-meter throw is being executed, the players of the opposing team must remain outside the free-throw line and at least 3 meters away from the 7-meter line, until the ball has left the thrower’s hand. If they do not do so, the 7-meter throw will be retaken if it does not result in a goal, but there is no personal punishment.
14:9 The 7-meter throw is to be retaken, unless a goal is scored, if the goalkeeper crosses his restraining line, i.e. the 4-meter line (1:7, 5:11), before the ball has left the thrower’s hand. However, it does not result in a personal punishment for the goalkeeper.
14:10 It is not permitted to change goalkeepers once the thrower is ready to take the 7-metre throw, standing in the correct position with the ball in hand. Any attempt to make a substitution in this situation is to be penalized as unsportsmanlike conduct (8:7c, 16:1b and 16:3d).
15:1 Prior to the execution, the thrower must be in the correct position prescribed for the throw. The ball must be in the hand of the thrower (15:6).
During the execution, except in the case of the goalkeeper throw (see 12:2) and the throw-off with throw-off area (10:3b), the thrower must have one part of a foot in constant contact with the floor until the ball is released (see, however, 10:3b). The other foot may be lifted and put down repeatedly (see also Rule 7:6). The thrower must remain in the correct position until the throw has been executed (15:7, 2nd and 3rd paragraph).
Comment:
Before the execution of a throw (except in the case of the goalkeeper throw), the thrower must be in an upright position, i.e. no other body parts than the feet are allowed to be in contact with the floor.
15:2 A throw is considered taken when the ball has left the hand of the thrower (see, however, 12:2, 10:3a, 2nd paragraph and 10:3b).
The thrower must not touch the ball again until it has touched another player or the goal (15:7, 15:8). See also further restrictions for situations under 14:6.
A goal may be scored directly from any throw, except that a direct ‘own goal’ cannot be scored through a goalkeeper throw if the ball is out of play (12:1) (i.e., by dropping the ball into one’s own goal).
15:3 The teammates must take up the positions prescribed for the throw in question (15:6).
The players must remain in correct positions until the ball has left the hand of the thrower, except as under 10:3a, 2nd paragraph (see, however, 10:3b).
The ball must not be touched by, or handed over to, a teammate during the execution (15:7, 2nd and 3rd paragraph).
15:4 The defending players must take up the positions prescribed for the throw and remain in correct position until the ball has left the hand of the thrower (see, however, 10:3b, 12:2 and 15:9).
Incorrect positions on the part of the defending players in connection with the execution of a throw-off, throw-in, or free throw must not be corrected by the referees if the attacking players are not at a disadvantage by taking the throw immediately. If there is a disadvantage, then the positions are to be corrected.
15:5 The referee must blow the whistle for the restart :
a) always in the case of a throw-off (10:3) or 7-meter throw (14:4);
b) in the case of a throw-in, goalkeeper-throw or free-throw :
• for a restart after a time-out;
• for a restart with a free-throw under Rule 13:4;
• when there has been a delay in the execution;
• after a correction of the player positions;
• after a verbal caution or a warning.
The referee may judge it appropriate, for the sake of clarity, to blow the whistle for the restart on any other occasion.
In principle, the referee shall not give the whistle signal for the restart unless and until the requirements for player positions under 15:1, 15:3 and 15:4 are met. (See, however, 13:7 2nd paragraph and 15:4 2nd paragraph). If the referee blows his whistle for a throw to be taken, despite incorrect positions on the part of players, then those players are fully entitled to intervene.
After the whistle signal the thrower must play the ball within 3 seconds.
15:6 Violations by the thrower or his teammates prior to the execution of a throw, i.e., typically in the form of incorrect positions or the touching of the ball by a teammate, shall lead to a correction. (See, however, 13:7 2nd paragraph).
15:7 The consequences of violations by the thrower or his teammates (15:1-3) during the execution of a throw depend primarily on whether the execution was preceded by a whistle signal for the restart.
In principle, any violation during an execution that was not preceded by a restart signal is to be handled through a correction and a retaking of the throw after a whistle signal. However, an advantage concept, in analogy with Rule 13:2, applies here. If the thrower’s team immediately loses possession after an incorrect execution, then the throw is simply considered to have been executed and play continues.
In principle, any violation during an execution after a restart signal is to be penalized. This applies, for instance, if the thrower jumps during the execution, holds on to the ball for more than 3 seconds, or moves out of the correct position before the ball has left his hand. It applies if the teammates move into illegal positions after the whistle signal but before the ball has left the thrower’s hands (Note 10:3, 2nd paragraph). In such cases, the initial throw is forfeited, and the opponents are awarded a free-throw (13:1a) from the place of the infraction (see, however, Rule 2:6). The advantage provision under Rule 13:2 does apply, i.e., if the thrower’s team loses possession of the ball before the referees have an opportunity to intervene, play continues.
15:8 In principle, any violation immediately following, but related to, the execution is to be penalized. This refers to a violation of 15:2, 2nd paragraph, i.e., the thrower touches the ball a second time before it has touched another player or the goal. It can take the form of a dribble, or grabbing the ball again after it is in the air or has been put down on the floor. This is sanctioned with a free-throw (13:1a) for the opponents. As in the case of 15:7 3rd paragraph, the advantage provision applies.
15:9 Except as indicated in Rules 14:8, 14:9, 15:4 2nd paragraph and 15:5 3rd paragraph, defending players who interfere with the execution of a throw for the opponents, for instance by not taking up a correct position initially or by moving into an incorrect position subsequently, shall be penalized. This applies regardless of whether it happens prior to the execution or during the execution (before the ball has left the thrower’s hand).
It also applies whether the throw was preceded by a whistle signal for the restart or not. Rule 8:7c applies, in conjunction with Rules 16:1b and 16:3d.
A throw that was negatively affected by a defender’s interference shall, in principle, be repeated.
16:1 A warning is the appropriate punishment for:
a) fouls that are to be punished progressively (8:3; compare however 16:3b and 16:6d);
b) unsportsmanlike conduct that is to be punished progressively (8:7).
Comments :
A player should not be given more than one warning, and the players of a team should not be given more than 3 warnings in total; thereafter, the punishment must be at least a 2-minute suspension. A player who has already had a 2-minute suspension should not subsequently be given a warning. No more than one warning in total should be given to the officials of a team.
16:2 The referee shall indicate the warning to the guilty player or official and to the timekeeper/ scorekeeper by holding up a yellow card. (hand signal no. 13).
16:3 A suspension (2 minutes) is the appropriate punishment:
a) for a faulty substitution, if an additional player enters the court, or if a player interferes in the game from the substitution area (4:5-6); note, however, Rule 8:10b (II);
b) for fouls such as those under 8:3, if the player and/or his team has already received the maximum number of warnings (see 16:1 Comment);
c) for fouls such as those under 8:4;
d) for unsportsmanlike conduct by a player as under 8:7, if the player and/or his team has already received the maximum number of warnings;
e) for unsportsmanlike conduct by a team official as under 8:7, if one of the officials on the team has already received a warning;
f) for unsportsmanlike conduct by a player or team official as under 8:8 (see also 4:6);
g) as a consequence of a disqualification of a player or team official (16:8, 2nd paragraph; see, however, 16:11b);
h) for unsportsmanlike conduct by a player before the game has been restarted, after he has just been given a 2-minute suspension (16:9a).
Comments :
It is not possible to give the officials of a team more than one 2-minute suspension in total.
When a 2-minute suspension is called against a team official in accordance with 16:3e, the official is allowed to remain in the substitution area and carry out his functions. However, the team’s strength on the court is reduced for 2 minutes.
16:4 After calling time-out the referee shall clearly indicate the suspension to the guilty player and to the timekeeper/scorekeeper through the prescribed hand signal, i.e. one arm raised with two fingers extended (hand signal no. 14).
16:5 A suspension is always for a playing time of 2 minutes; the third suspension for the same player also always leads to a disqualification (16:6d).
The suspended player is not allowed to participate in the game during his suspension time, and the team is not allowed to replace him on the court.
The suspension period begins when play is restarted with a whistle signal.
A 2-minute suspension carries over to the second half of the game if it has not been completed by the end of the first half. The same applies from the normal playing time to overtime and during overtime. An unexpired 2-minute suspension at the end of overtime means that the player is not entitled to participate in a subsequent tie-breaker, such as 7-meter-throws in accordance with 2:2 Comment.
16:6 A disqualification is the appropriate punishment:
a) for fouls under 8:5 and 8:6;
b) for seriously unsportsmanlike conduct under 8:9 and extremely unsportsmanlike conduct under 8:10, by a player or team official, on or outside the court;
c) or unsportsmanlike conduct by any one of the officials of a team under 8:7, after they have collectively already received both a warning and a 2-minute suspension in accordance with 16:1b and 16:3e;
d) as a consequence of a third suspension to the same player (16:5);
e) for significant or repeated unsportsmanlike conduct during a tie-breaker such as 7-metre throwing (2:2 Comment and 16:10).
16:7 After calling a time-out, the referees shall clearly indicate the disqualification to the guilty player or team official, and to the timekeeper/scorekeeper, by holding up a red card (hand signal no. 13, see also Rule 16:8).
16:8 A disqualification of a player or team official is always for the entire remainder of the playing time. The player or official must leave the court and the substitution area immediately. After leaving, the player or official is not allowed to have any form of contact with the team.
The disqualification of a player or a team official, on or off the court, during the playing time, always carries with it a 2-minute suspension for the team. This means that the team’s strength on the court is reduced by one (16:3f). The reduction on the court will, however, last for 4 minutes if a player has been disqualified in the circumstances indicated in Rule 16:9b-d.
A disqualification reduces the number of players, or officials, which is available to the team (except as in 16:11b). The team is, however, allowed to increase the number of players on the court again following the expiration of the 2-minute suspension.
As noted in Rules 8:6 and 8:10a-b, disqualifications in accordance with these rules are to be reported in writing to the responsible authorities for further action. In such cases, the ‘responsible team officials’, and the delegate (see Clarification No. 7), shall be informed immediately after the decision.
For this purpose, the referee also shows the blue card as information after holding up the red card.
16:9 If a player or team official is guilty of more than one violation simultaneously or in direct sequence before the game has been restarted and these violations warrant different punishments, then in principle, only the most severe one of these punishments shall be given.
There are however the following specific exceptions where in all cases the team must play at reduced strength on the court for 4 minutes:
a) if a player who has just been given a 2-minute suspension is guilty of unsportsmanlike conduct before the game restarted, then the player is given an additional 2-minute suspension (16:3g); if the additional suspension is the player’s third one, then the player is to be disqualified;
b) if a player who has just been given a disqualification (directly or because of a third suspension) is guilty of unsportsmanlike conduct before the game is restarted, then the team is given a further punishment so that the reduction will be for 4 minutes (16:8, 2nd paragraph);
c) if a player who has just been given a 2-minute suspension is guilty of seriously or extremely unsportsmanlike conduct before the game is restarted, then the player is furthermore disqualified (16:6b); these punishments combined lead to a 4-minute reduction (16:8, 2nd paragraph);
d) if a player who has just been given a disqualification (directly or because of a third suspension) is guilty of seriously or extremely unsportsmanlike conduct before the game is restarted, then the team is given a further punishment so that the reduction will be for 4 minutes (16:8, 2nd paragraph).
16:10 The punishments for actions during the playing time are established in Rules 16:1, 16:3 and 16:6.
In the concept ‘playing time’ all intermissions, time-outs, team time-outs and overtime periods are included. In all other forms of tie-breakers (e.g., 7-metre throws), only Rule 16:6 applies.
In this way any form of significant or repeated unsportsmanlike conduct will prevent the further participation of the player concerned (see Rule 2:2 Comment).
16:11 Unsportsmanlike conduct, seriously unsportsmanlike conduct, extremely unsportsmanlike conduct, or any form of particularly reckless actions (see Rules 8:6-10) on the part of a player or team official, taking place on the premises where a game is played but outside the playing time, shall be punished as follows:
Before the game:
a) a warning shall be given in the case of unsportsmanlike conduct under Rules 8:7-8;
b) a disqualification of the guilty player or team official shall be given in the case of action deemed to fall under Rules 8:6 and 8:10a, but the team is allowed to start with 14 players and 4 officials; Rule 16:8, 2nd paragraph applies only for violations during the playing time; accordingly, the disqualification does not carry with it a 2-minute suspension.
Such punishments for violations prior to the game can be implemented at any time during the game, whenever the guilty person is discovered to be a participant in the game, as this fact may not be possible to establish yet at the time of the incident.
After the game:
c) a written report.
17:1 Two referees with equal authority shall be in charge of each game. They are assisted by a timekeeper and a scorekeeper.
17:2 The referees monitor the conduct of the players and team officials from the moment they enter the premises until they leave.
17:3 The referees are responsible for inspecting the playing court, the goals, and the balls before the game starts; they decide which balls will be used (1 and 3:1).
The referees also establish the presence of both teams in proper uniforms. They check the score sheet and the equipment of the players. They ensure that the number of players and officials in the substitution area is within the limits, and they establish the presence and identity of the «responsible team official», for each team. Any discrepancies must be corrected (4:1-2 and 4:7-9).
17:4 The coin toss is undertaken by one of the referees in the presence of the other referee and the ‘responsible team official’ for each team, or a team official or player on behalf of the ‘responsible team official’.
17:5 In principle, the entire game shall be conducted by the same referees.
It is their responsibility to ensure that the game is played in accordance with the rules, and they must penalize any infractions (see, however, 13:2 and 14:2).
If one of the referees becomes unable to finish the game, the other referee will continue the game alone.
17:6 If both referees whistle for an infraction and agree about which team should be penalized but have different opinions as to the severity of the punishment, then the most severe of the two punishments shall be given.
17:7 If both referees whistle for an infraction, or the ball has left the court, and the two referees show different opinions as to which team should have possession, then the joint decision that the referees reach after consulting with each other will apply. If they do not manage to reach a joint decision, then the opinion of the court referee will prevail.
A time-out is obligatory. Following the consultation between the referees, they give clear hand signals and the game is restarted after whistle signal (2:8d, 15:5).
17:8 Both referees are responsible for keeping the score. They also take notes about warnings, suspensions, disqualifications, and exclusions.
17:9 Both referees are responsible for controlling the playing time. If there is any doubt about the accuracy of the timekeeping, the referees reach a joint decision (see also 2:3).
17:10 The referees are responsible for ensuring after the game that the score sheet is completed correctly. Disqualifications of the type indicated in Rules 8:6 and 8:10 must be explained in the match report.
17:11 Decisions made by the referees on the basis of their observations of facts or their judgments are final.
Appeals can be lodged only against decisions that are not in compliance with the rules.
During the game, only the respective «responsible team officials» are entitled to address the referees.
17:12 The referees have the right to suspend a game temporarily or permanently. Every effort must be made to continue the game, before a decision is taken to suspend it permanently.
17:13 The black uniform is primarily intended for the referees.
17:14 The referees and the delegates may use electronic equipment for their internal communication.
18:1 In principle, the timekeeper has the main responsibility for the playing time, the time-outs, and the suspension time of suspended players.
The scorekeeper has the main responsibility for the team rosters, the score sheet, the entering of players who arrive after the game has started, and the entering of players who are not entitled to participate.
Other tasks, such as the control of the number of players and team officials in the substitution area, and the exit and entry of substituting players, as well as counting the number of attacks (this decision is regarded as based on their observation of facts) after treatment given to a player on the court, are regarded as joint responsibilities.
Generally, only the timekeeper (and, when applicable, a Technical Delegate) should interrupt the game when this becomes necessary.
See also Clarification No. 7 regarding proper procedures for the interventions of the timekeeper/scorekeeper when fulfilling some of the responsibilities indicated above.
18:2 If there is no public scoreboard clock available, then the time- keeper must keep the «responsible team official» for each team informed about how much time has been played or how much time is left, especially following time-outs.
If there is no scoreboard clock with automatic signal available, the timekeeper assumes the responsibility for giving the final signal at half-time and at the end of the game (see 2:3).
If the public scoreboard is not capable of displaying also the suspension time (at least three per team during the games), the timekeeper shall display a card on the timekeeper’s table, showing the expiration time of each suspension, together with the player’s number.
When a throw-in or free throw is called, the referees must show immediately the direction for the throw that is to follow (signals 7 or 9).
Thereafter, as applicable, the appropriate obligatory hand signal(s) should be given, to indicate any personal punishment (signals 13-14).
If it seems that it would also be useful to explain the reason for a free-throw or 7-metre throw decision, then the applicable one of signals 1-6 and 11 could be given for the sake of information. Signal 11 should, however, always be given in those situations where a free-throw decision for passive play was not preceded by signal 17.
Signals 12, 15 and 16 are mandatory in those situations where they apply.
Signals 8, 10 and 17 are used as deemed necessary by the referees.

















Free-Throw Execution after the Final Signal (2:4-6)
In many cases, the team that has the opportunity to execute a free-throw after the playing time has expired is not really interested in trying to score a goal, either because the outcome of the game is already clear or because the position for the free-throw is too far away from the goal of the opponents. Although technically the rules require that the free-throw be executed, the referees should show good judgment and consider the free-throw taken if a player who is in the approximately correct position simply lets the ball drop or hands it to the referees.
In those cases where it is clear that the team wants to try to score a goal, the referees must try to find a balance between allowing this opportunity (even though it is a very small one) and ensuring that the situation does not deteriorate into a time-consuming and frustrating «theater». This means that the referees should get the players from both teams into correct positions firmly and quickly so that the free-throw can be executed without delay. The new restrictions in Rule 2:5 regarding player positions and substitutions must be enforced (4:5 and 13:7).
The referees must also be very alert to other punishable violations by the two teams. Persistent encroachment by the defenders must be punished (15:4, 15:9, 16:1b, 16:3d). Moreover, the attacking players often violate the rules during the execution, e.g. one or more players cross the free throw line after the whistle but before the throw (13:7, 3rd paragraph), or the thrower actually moves or jumps when throwing (15:1, 15:2, 15:3).
It is very important not to allow any goals scored illegally.
Time-Out (2:8)
Apart from the situations indicated in Rule 2:8, where a time-out is obligatory, the referees are expected to use their judgment regarding the need for time-outs also in other situations. Some typical situations where time-outs are not obligatory but nevertheless tend to be given in normal circumstances are:
a) there are external influences, e.g. the court must be wiped;
b) a player seems to be injured;
c) a team is clearly wasting time, e.g. when the team is delaying the execution of a formal throw, or when a player is throwing the ball away or not releasing it;
d) if the ball touches the ceiling or a fixture above the court (11:1), and the ball is deflected so that it goes far away from the location of the resulting throw-in, causing an unusual delay;
e) replacing a court player with a goalkeeper in order to execute a goalkeeper throw.
When determining the need for a time-out in these and other situations, the referees should foremost take into consideration whether an interruption of the game without a time-out would create an unfair disadvantage for one of the teams. For instance, if a team is leading by a very clear margin late in the game, then it might not be necessary to make a time-out during a brief interruption to wipe the court. Similarly, if the team that would be disadvantaged by the lack of a time-out is the team that, for some reason, is itself causing a delay or wasting time, then there is obviously no reason for a time-out.
Another important factor is the expected duration of the interruption. The length of an interruption caused by an injury is often difficult to estimate, so it may then be safer to call a time-out. Conversely, the referees should not be too quick to call a time-out just because the ball has left the playing court. In such cases the ball is often back and ready to be played almost immediately. If not, the referees should concentrate on getting a reserve ball into play quickly (3:4), precisely in order to make a time-out unnecessary.
The obligatory time-out in connection with 7-meter throws has been removed. It may still be necessary to give a time-out based on subjective judgment on some occasions, in accordance with the principles just discussed. This may involve situations where one of the teams clearly delays the execution, including for instance through a substitution of the goalkeeper or the thrower.
Team Time-Out (2:10)
Each team has the right to receive one 1-minute team time-out in each half of the regular playing time (but not in overtime).
A team that wishes to request a team time-out must do so by having a team official place a green card on the table in front of the timekeeper. (It is recommended that the green card measures about 15 x 20 cm and has a large «T» on each side).
A team may request their team time-out only when it has possession of the ball (when the ball is in play or during an interruption). Provided that the team does not lose possession before the timekeeper has time to whistle (in which case the green card would be returned to the team), the team will be granted the team time-out immediately.
The timekeeper then interrupts the game by blowing the whistle, and stops the clock (2:9). He gives the hand signal for time-out (no. 16) and points with a stretched arm at the team that requested the team time-out.
(If necessary, due to noise and commotion, the timekeeper stands up while doing so.) The green card is placed on the table, on the side of the team that requested the team time-out, and remains there during the time-out.
The referees acknowledge the team time-out, and the timekeeper starts a separate clock controlling the duration of the team time-out. The scorekeeper enters the time of the team time-out in the score sheet for the team that requested it.
During the team time-out the players and team officials remain at the level of their substitution areas, either on the court or in the substitution area. The referees stay in the center of the court, but one of them may briefly go to the timekeeper's table for consultation.
For the purpose of punishments under Rule 16, a team time-out is defined as being part of the playing time (16:10), so any unsportsmanlike conduct and other infractions are punished in the normal way. It is irrelevant in this context, if the player/official concerned is on or off the court. Accordingly, a warning, suspension or disqualification under Rules 16:1-3 and 16:6-9 can be given for unsportsmanlike conduct (8:7-10) or for action falling under Rule 8:6b.
After 50 seconds the timekeeper gives an acoustic signal indicating that the game is to be continued in 10 seconds.
The teams are obliged to be ready to resume play when the team time-out expires. The game is restarted either with the throw that corresponds to the situation that existed when the time-out was granted or, if the ball was in play, with a free-throw for the team requesting the team time-out from the place where the ball was at the time of the interruption.
When the referee blows the whistle the timekeeper starts the clock.
A team may request the team time-out directly through pushing a button (buzzer) on an electronic device instead of using green cards. The buzzer is directly connected to the official scoreboard system. Once the buzzer has been pushed, the time will be directly stopped. In order to make all parties aware of the team time-out, it is also indicated by an audio signal. For further details, please refer to the Electronic Team Time-Out Regulations.
Comments:
Each team has the right to receive a maximum of three team time-outs during regular playing time but not during overtime. No more than two team time-outs may be granted in each half of the regular playing time. Between two team time-outs of a team, the opponent must be at least once in possession of the ball. 3 green cards, bearing numbers 1, 2, and 3 respectively, are available for each team.
The teams receive cards bearing numbers ‘1’ and ‘2’ in the first half of the game and the cards no. 2 and no. 3 in the second half provided they received no more than one team time-out in the first half. In case they received two team time-outs in the first half, they receive only green card no. 3.
Within the last five minutes of the regular playing time only one team time-out per team is allowed.
Passive Play (7:11-12)
A. General Guidelines
The application of the rules regarding passive play has the objective of preventing unattractive methods of play and intentional delays in game. This requires that the referees throughout the game recognize and judge passive methods in a consistent manner.
Passive methods of play may arise in all phases of a team’s attack, i.e. when the ball is moved down the court, during the build-up phase, or during the finishing phase.
Passive ways of playing may be used relatively more frequently in the following situations :
• a team is narrowly in the lead towards the end of the game;
• a team has a player suspended;
• when the ability of the opponent is superior, especially on defense.
The criteria mentioned in the following specifications rarely apply alone, but must generally be judged in their entirety by the referees. In particular, the impact of active defensive work in conformity with the rules must be taken into account.
B. The Utilization of the Forewarning Signal
The forewarning signal should be shown particularly in the following situations :
B1. Forewarning signal when substitutions are made slowly or when the ball is moved slowly down the court
Typical indications are:
• players are standing around in the middle of the court waiting for substitutions to be completed;
• a player is delaying the execution of a free-throw (by playing around with the ball or pretending not to know the correct spot), throw-off (by a slow recovery of the ball by the goalkeeper, by an erratic pass to middle, or by slow walking with the ball to the middle), goalkeeper-throw, or throw-in, after the team has previously been admonished for such delaying tactics;
• a player is standing still bouncing the ball;
• the ball is played back into the team’s own half of the court, even though the opponents are not putting on any pressure;
B2. Forewarning signal in connection with a late substitution during the build-up phase
Typical indications are:
• all players have already taken up their attacking positions;
• the team starts the build-up phase with a preparatory passing play;
• not until this stage does the team undertake a substitution.
Comment :
A team which has attempted a rapid counter-attack from its own half of the court, but has failed to get to an immediate scoring opportunity after reaching the opponents’ half of the court, must be allowed to undertake a quick substitution of players at that stage.
B3. During an excessively long build-up phase
In principle, a team must always be allowed a build-up phase with a preparatory passing play before they can be expected to start a targeted attacking situation.
Typical indications of an excessively long build-up phase are :
• the team’s attack does not lead to any targeted attacking action;
Comment :
A targeted attacking action exists particularly when the attacking team uses tactical methods to move in such a way that they gain spatial advantage over the defenders, or when they increase the pace of the attack in comparison with the build-up phase.
• players are repeatedly receiving the ball while standing still or moving away from the goal;
• repeated bouncing of the ball while standing still;
• when confronted by an opponent, the attacking player turns away prematurely, waits for the referees to interrupt the game, or gains no spatial advantage over the defender;
• active defensive actions: active defensive methods preventing the attackers from increasing the pace because the defenders block the intended ball movements and running paths;
• a special criterion for excessively long build-up phases is when the attacking team achieves no clear increase in pace from the build-up phase to the finishing phase.
C. How the Forewarning Signal should be shown
If a referee (either the court referee or the goal-line referee) recognizes the emergence of passive play, he lifts the arm (hand signal no. 17), to indicate the judgment that the team is not trying to get into a position to take a shot on goal. The other referee should also give the forewarning signal.
The forewarning signal conveys that the team in possession is not making any attempt to create a scoring opportunity, or that it is repeatedly delaying the restart of the game.
The hand signal is maintained until:
• the attack is over, or
• the forewarning signal is no longer valid (see comments below).
An attack begins when the team gets into possession of the ball, and is considered over when the team scores a goal or loses possession.
The forewarning signal normally applies for the entire remainder of the attack. However, during the course of an attack, there are two situations where the judgement of passive play is no longer valid, and the forewarning signal must be stopped immediately :
1. the team in possession takes a shot on goal and the ball rebounds to the team from the goal or the goalkeeper (directly or in the form of a throw-in) or
2. a player or team official of the defending team is given a progressive punishment under Rule 16 due to a rules infraction or unsportsmanlike conduct. In these two situations, the team in possession must be allowed a new build-up phase.
In these two situations, the team in possession must be allowed a new build-up phase.
D. After the forewarning signal has been shown
After showing the forewarning signal, the referees should allow the team in possession of the ball some time to change their action. In this regard, the skill level in different age and performance categories must be taken into account.
The team forewarned should thus be allowed the possibility to prepare a targeted attacking action towards the goal.
If the team in possession does not make a recognizable attempt to get into position to take a shot on goal (decision-making criteria see D1 and D2), then one of the referees decides that this is passive play at the latest when no shot on goal is executed after 4 passes (7:11-12).
The following actions are not considered as passes:
• If an attempted pass cannot be controlled due to a penalized foul by a defending player.
• If an attempted pass is deflected by a defending player out over the side line or the outer goal line.
• A throwing attempt that is blocked by the opponent.
Decision-making criteria after showing the forewarning signal:
D1. The attacking team:
• no clear increase in pace;
• no targeted action towards the goal;
• 1-on-1 actions where no spatial advantage is achieved;
• delays when playing the ball (e.g., because the passing routes are blocked by the defending team).
D2. The defending team:
• the defending team tries to prevent an increase in pace or a targeted attacking action, through correct and active defensive methods;
• if the defending team tries to interrupt a pass sequence of the attacking team by committing infractions in accordance with Rule 8:3, this behaviour has to be consistently punished progressively.
D3. Notes concerning the maximum number of passes
D3a. Before the execution of the 4th pass:
• If the referees decide a free throw or a throw-in to the attacking team when the forewarning signal has been shown, it does not interrupt the count of passes.
• Similarly if a pass or a shot on goal is blocked by a court player of the defending team and the ball goes to the attacking team (even as a goalkeeper throw), it does not interrupt the count of passes.
D3b. After the execution of the 4th pass:
• If a free throw, a throw-in (or a goalkeeper throw) is awarded to the attacking team after the 4th pass, the team has the possibility of combining a throw with one additional pass to finish the attack.
• The same applies if the throw executed after the 4th pass is blocked by the defending team and the ball is directed to an attacking player or passes the side line or the outer goal line. In this case, the attacking team has the possibility of finishing the attack by making one additional pass.
E. Appendix
Indications of a reduction of pace
• Action sideways and not in depth towards the goal
• Frequent diagonal running in front of the defenders without putting any pressure on them
• No action in depth, such as confronting an opponent 1-on-1 or passing the ball to players between the goal-area line and the free throw line
• Repeated passing between two players with no clear increase of pace or actions towards the goal
• Passing of the ball with all positions involved (wing players, pivot and back-court players) with no clear increase of pace or recognizable actions towards the goal
Indications of 1-on-1 actions where no spatial advantage is gained
• 1-on-1 action in a situation where it is obvious that there is no room for a break-through (several opponents block the room for a break-through.)
• 1-on-1 action without any aim to break through towards the goal
• 1-on-1 action with the objective of simply being awarded a free throw (e.g., letting oneself ‘get stuck’, or ending the 1-on-1 action even though it might have been possible to break through)
Indications of active defensive methods in conformity with the rules
• Trying not to commit a foul, so as to avoid an interruption in the game
• Obstructing the running path of the attacker, perhaps by using two defenders
• Moving forward to block the passing routes
• Defenders moving forward to force the attackers further back in the court
• Provoking attackers to pass the ball far back into harmless positions
Throw-Off (10:3)
Throw-Off Execution
As a guiding principle for the interpretation of Rule 10:3, the referees should keep in mind the objective of encouraging teams to make use of a quick throw-off. This means that the referees should avoid being pedantic and should not search for opportunities to interfere with, or penalize, a team trying to throw quickly.
For instance, the referees must avoid letting note-taking or other tasks interfere with their readiness to check the player positions quickly. The court referee should be ready to whistle at the very moment when the thrower reaches the correct position, assuming that there is no clear need for corrections of other player positions. The referees must also keep in mind that the teammates of the thrower are allowed to move across the center line as soon as the whistle is blown. (This is an exception from the basic principle for the execution of formal throws.)
Execution without throw-off area
Although the rule states that the thrower must step on the center line and be within 1.5 meter from the center, the referees should not be excessively precise and concerned about centimeters. The main thing is to avoid unfairness and uncertainty for the opponents as regards when and where the throw-off is taken.
Moreover, most courts do not have the center point marked, and some courts may even have the center line interrupted due to advertising at the center. In such cases, both the thrower and the referee will obviously need to estimate the correct position, and any insistence on exactness would then be unrealistic and inappropriate.
Definition of Clear Chance of Scoring (14:1)
For the purposes of Rule 14:1, a clear chance of scoring exists when :
a) a player who already has ball and body control at the goal-area line of the opponents has the opportunity to shoot on goal, without any opponent being able to prevent the shot with legal methods.
This also applies if the player does not yet have the ball but is ready for an immediate reception of the ball; there must not be an opponent in a position to prevent the reception of the ball with legal methods.
b) a player who has ball and body control is running (or dribbling) alone towards the goalkeeper in a counter-attack, without any other opponent being able to come in front of him and stop the counter-attack.
This also applies if the player does not yet have the ball but is ready for an immediate reception of the ball, and the opposing goalkeeper through a collision as under 8:5 Comment prevents the reception of the ball; in this special case, the positions of the defending players are irrelevant.
c) a goalkeeper has left his goal area and an opponent with ball and body control has a clear and unimpeded opportunity to throw the ball into the empty goal.
Intervention by the Timekeeper or a Delegate (18:1)
If the timekeeper or a delegate intervenes, when the game is already interrupted, then the game is restarted with the throw that corresponds to the reason for the interruption.
If the timekeeper or a delegate intervenes, and thereby interrupts the game when the ball is in play, then the following regulations apply:
A. Faulty substitution of illegal entry by a player (Rule 4:2-3,5-6)
The timekeeper (or delegate) must interrupt the game immediately, without regard for the ‘advantage’ concept under Rules 13:2 and 14:2. If due to such an interruption, due to violation by the defending team, a clear chance of scoring is destroyed, then a 7-metre throw must be awarded in accordance with Rule 14:1a. In all other cases, the game is restarted with a free throw.
The guilty player is punished in accordance with Rule 16:3a. However, in the case of illegal entry under Rule 4:6, during a clear chance of scoring, then the player is punished in accordance with Rule 16:6b in conjunction with Rule 8:10b.
B. Interrupting for other reasons, e.g., unsportsmanlike conduct in the substitution area
1. Intervention by the Timekeeper
The timekeeper should wait until the next interruption in the game and then inform the referee.
If nevertheless the timekeeper interrupts the game while the ball is in play, then the game is restarted with a free throw for the team that was in possession at the time of the interruption.
If the interruption is due to a violation by the defending team, and thereby a clear chance of scoring is destroyed, then a 7-metre throw must be awarded in accordance with Rule 14:1b.
(The same applies if the timekeeper interrupts the game due to a request for a team time-out, and the referees refuse the team time-out because the timing is wrong. If a clear chance of scoring is destroyed due to the interruption, then a 7-metre throw must be awarded).
The timekeeper does not have the right to pronounce a punishment against a player or a team official. The same applies to the referees, if they have not themselves observed the violation. In such a case, they can only give an informal caution. If the reported violation falls under Rules 8:6 or 8:10, they must submit a written report.
2. Intervention by a delegate
Delegates who are on duty in a game, have the right to inform the referees about a possible decision in violation of the rules (except in the case of a referee decision on the basis of an observation of facts) or about a violation of the substitution area regulations.
The delegate may interrupt the game immediately. In this case, the game is restarted with a free throw for the team that did not commit the violation that led to the interruption.
If the interruption is caused by a violation from the defending team, and the interruption causes a clear scoring chance to be destroyed, then a 7-metre throw in accordance with Rule 14:1a must be awarded
The referees are obligated to give out personal punishments in accordance with the instructions of the delegate.
The facts related to a violation of Rules 8:6 or 8:10 are to be reported in writing.
Injured Player (4:11)
If a player seems to be injured on the court, the following measures have to be taken:
a) If the referees are absolutely sure that the injured player needs medical treatment on the field, they will immediately show the hand signals no. 15 and 16. Thus, the player has to meet the regulations of Rule 4:11 2nd paragraph after receiving treatment.
In all the other cases, the referees will ask the player to go out to receive treatment outside the court. If this is not possible for the player concerned, the referees will show the hand signals no. 15 and 16. Rule 4:11, 2nd paragraph is applicable.
Infractions of these regulations will be punished due to unsportsmanlike conduct.
If a player, who has to leave the playing court during three attacks, is punished with a 2-minute suspension, he is allowed to re-enter the court at the end of this suspension, regardless of the number of attacks played.
If team officials refuse to provide the necessary treatment of a player, the ‘responsible team official’ is to be punished progressively (see Rule 4:2, 3rd paragraph).
b) The timekeeper and the scorekeeper or the delegates are responsible for counting the number of attacks. They inform the team concerned as soon as the player is allowed to re-enter the court.
An attack starts with the possession of the ball and ends when a goal is scored or the team in attack loses the ball.
If the team is in possession of the ball when its player needs treatment, this attack is considered as the first attack.
c) Rule 4:11 2nd paragraph does not apply in the following cases:
• if the required treatment of injury on the playing court is the result of an illegal action by an opposing player who has been punished progressively by the referees;
• if the goalkeeper’s head is hit by a ball and treatment inside the court is necessary.

1. The substitution areas are situated outside the sideline, to the left and right of the extension of the center line, up to end of the respective team benches, and also behind the benches if there is space.
The regulations for IHF and continental federation events prescribe that the team benches shall start at a distance of 3.5 meters from the center line.
No objects of any kind may be placed at the side line in front of the team benches (for at least 8 meters from the center line).
2. Only the players and team officials entered in the score sheet are allowed to be in the substitution area (4:1-2).
If an interpreter is needed, he must take up a position behind the team bench.
3. The team officials in the substitution area must be fully dressed in sportswear or civilian clothing. Colors which may cause confusion with the court players of the opposing team are not allowed.
4. The timekeeper and scorekeeper shall support the referees in monitoring the occupancy of the substitution area before and during the game.
If before the game there are any infringements of the rules as regards the substitution area, the game may not start until the infringements have been remedied. If these rules are infringed during the game, the game may not be continued after the next interruption until the matter has been resolved.
5. The team officials have the right and duty to guide and manage their team also during the game, in a fair and sporting spirit within the framework of the rules. In principle, they should sit on the team bench.
However, the officials are permitted to move around within the ‘coaching zone’. The ‘coaching zone’ is the area directly in front of the bench and, if this is feasible, also directly behind it.
The movements and the positioning in the ‘coaching zone’ are allowed for the purposes of giving tactical advice and to provide medical care. In principle, only one official of the team is allowed to stand or move at a time. However, his position or his behavior shall not interfere with the actions of the players who are on the court. In case of an infraction of these regulations, the official is to be punished progressively.
It is, of course, permitted for one team official to leave the ‘coaching zone’ when he immediately wants to submit the ‘green card’ to request a team time-out. However, the team official is not allowed to leave the ‘coaching zone’ with the ‘green card’ and stand waiting at the table for the moment to request the team time-out.
The ‘responsible team official’ may also leave the ‘coaching zone’ in special situations, for instance, for necessary contact with the timekeeper or scorekeeper.
In principle, players in the substitution area should sit on the substitution bench.
The players are however permitted to:
• move around behind the bench to warm up, without ball, provided that there is sufficient space and that it is not disruptive.
It is not permitted for team officials or players to:
• interfere with or insult referees, delegates, timekeeper/scorekeeper, players, team officials, or spectators, by behaving in a provocative, protesting, or otherwise unsportsmanlike manner (speech, facial expression or gestures);
• leave the substitution area in order to influence the game.
Team officials and players are generally expected to remain in the substitution area of their team. If a team official nevertheless leaves the substitution area for another position, he loses the right to guide and manage his team and he must return to the substitution area to regain his right.
More generally, players and team officials remain under the jurisdiction of the referees throughout the game, and the normal rules for personal punishments apply also if a player or official decides to take up a position away from the court and the substitution area. Therefore, unsportsmanlike conduct, seriously unsportsmanlike conduct, and extremely unsportsmanlike conduct are to be punished in the same manner as if the violation had taken place on the court or in the substitution area.
6. If the Substitution Area Regulations are infringed, the referees or the delegates are obliged to act in accordance with the Rules 4:2 3rd paragraph, 16:1b, 16:3d-f or 16:6b-d (warning, suspension, disqualification).
a) The playing court consists of a rectangle which measures 40 x 20m. It should be checked by measuring the length of the two diagonals. From the outer side of one corner to the outside of the opposite corner they should measure 44.72m. The length of the diagonals for one half of the court should measure 28.28m. from the outside of each of the corners to the opposite outer middle of the center line.
The playing court is provided with marking lines which are called «lines». The width of the goal lines (between the goalposts) is 8cm like the goalposts, all other lines have a width of 5cm. Lines which separate adjacent areas of the playing court can be replaced by a change in colors between the adjacent areas.
b) The goal area in front of the goals consists of a 3 x 6m rectangle and two connecting quarter circle sectors each with a radius of 6m. It is constructed by drawing a 3m long line parallel to the goal line at a distance of 6m from the rear edge of the goal line to the front edge of the goal-area line. On both sides this line continues in two quarter-circle arcs with the center at the rear inside edge of the respective goalposts and with a radius of 6m. The lines and arcs which enclose the goal area are called the goal area line. The outer distance between the points where the two arcs meet the outer goal line in this way will measure 15m.
c) The broken free-throw line (9m line) is made parallel and concentric to the goal-area line with a 3m larger distance from the goal line.
The segments as well as the spaces between them measure 15cm.
The segments should be cut off right-angled and radially respectively. The measurements of the curved segments are taken over the outer chord.
d) The 1m long 7-meter line is drawn directly in front of the goal, parallel to the goal line, at a distance of 7m from the rear edge of the goal line to the front edge of the 7m line.
e) The goalkeeper’s restraining line (the 4m line) directly in front of the goal is 15cm long. It is parallel to, and 4m away from, the goal line measured from the rear edge of the goal line to the front edge of the 4m line, which means that the widths of both lines are included in this measure.
f) The playing area should be surrounded by a safety zone of at least 1m along the side lines and 2m behind the outer goal lines.
g) The goal is placed in the center of each outer goal line. The goals must be firmly attached to the floor or to the wall behind them. The interior measures are 3m in width and 2m in height.
The goal frame must be a rectangle, which means that the inside diagonals will measure 360.5cm (max. 361cm – min. 360cm, in one and the same goal the difference must be maximum 0.5cm). The rear side of the goalposts shall be in line with the rear edge of the goal line (and the outer goal line), which means that the front side of the goalposts is placed 3cm in front of the outer goal line.
The goalposts and the horizontal crossbar which joins them shall be made of a uniform material (e.g. wood, light metal or synthetic material) and have a square cross section of 8cm with rounded edges with a rounding radius of 4±1mm. On the three sides which are visible from the court, the goalposts and the crossbar must be painted in bands of two colors which contrast clearly with each other and with the background; the two goals on one and the same playing court must have the same colors.
The color bands of the goals measure in the corner between posts and bar 28cm in each direction in the same color. All other color bands shall be 20cm long. The goals must have a net, called goal net, which must be attached in such a way that a ball thrown into the goal cannot immediately rebound or pass through the goal. If necessary, an additional net, placed in the goal behind the goal line can be used. The distance from the goal line to this additional net should be approximately 70cm, but minimum 60cm.
h) The depth of the goal net should at the top be 0.9m behind the goal line, and at the bottom 1.1m, both measures with a tolerance of ± 0.1m. The size of the meshes should not be more than 10 x 10cm. The net must be fixed to the post and the crossbar at least at every 20cm. It is allowed to bind together the goal net and the additional net in such a way that no ball can go between the two nets.
i) Behind the goal in the middle of the outer goal line at a distance of approximately 1.5m, there should be a vertical barrage net with a length of 9 - 14m and a height of 5m from the floor.
j) In the middle of the substitution area at one of the side lines the table for the timekeeper is placed. The table of a length of max. 4m should be placed 30-40cm above the floor of the playing court in order to secure the field of vision.
k) All measurements without specification of a tolerance must correspond to the ISO-Norm (International Standard Organization -ISO 27681:1989).
l) Handball goals are standardized by the European Committee for Standardization, CEN (Comité Européen de Normalisation) as EN 749 in connection with EN 202.10-1.
The restraining line of the ‘coaching zone’ is provided for information purposes.
This line is 50 cm long and is drawn at a distance of 350 cm (outside the court, parallel to the Centre line). It begins at a distance of 30 cm at the outside of the side line (recommended dimensions).
The goals must be firmly attached to the floor or the walls behind them, or provided with an anti-overturn system. This new provision is approved with the objective to avoid accidents.
If the goalkeeper is injured in connection with a free throw after the final signal, the defending team is permitted to substitute the goalkeeper. This exception is not applicable to defensive field players.
In case of infractions or unsportsmanlike conduct by defenders during the execution of a free throw or 7-metre throw after the final signal, these defenders must be punished personally under Rules 16:3, 16:6 or 16:9. The throw has to be repeated (Rule 15:9, paragraph 3). Rule 8:10c is not applicable in such cases.
The start of the last five minutes of the playing time begins when the clock indicates 55:00 or 05:00.
The organizers have the right to allow the use of reserve balls that are not placed at the timekeeper’s table. The use of a reserve ball is decided by the referees according to Rule 3:4.
In the event that a team has not exhausted the maximum number of players (Rule 4:1) or officials (Rule 4:2) permitted, it is allowed:
• to register someone as an official who was initially registered as a player
• to register someone as a player who was initially registered as an official
The maximum number of players and officials respectively must not be exceeded.
The player’s or the official’s original function shall be deleted in the match report. It is not permitted to replace a player or an official in his original function which has meanwhile been deleted. Furthermore it is not allowed to delete a participant having a certain function in order to make a substitution in compliance with the maximum number permitted. It is not allowed to register a person as both a player and an official.
Personal punishment resulting from changing the function (warning, suspension) shall be considered for both the personal quota and the ‘player’ and ‘official’ quota respectively.
Players shall always leave and enter the court over their own team’s substitution line. Injured players who leave the court when playing time was interrupted are exempted.
Those players must not be forced to leave the court over the substitution line, where it is obvious that they need medical treatment inside the substitution area or in the changing rooms. Furthermore the referees should allow the substitute player to enter the court before the injured player has left the court in order to keep interruption to a minimum.
If an additional player enters the court without a substitution, there shall be a 2-minute suspension for the player.
If it is not possible to identify the guilty player, the following steps shall be taken:
• The delegate or the referees respectively advise the ‘responsible team official’ to name the guilty player.
• The named player shall receive the 2-minute suspension as a personal punishment.
• In the event that the ‘responsible team official’ refuses to name the guilty player, the delegate or the referees respectively shall name a player. The named player shall receive a 2-minute suspension as a personal punishment.
Comments:
• Only players who are on the court at the time of the game interruption may be named the ‘guilty player’.
• In case the ‘guilty player’ receives the third suspension, he shall be disqualified according to Rule 16:6d.
An infringement regarding Rules 4:7 and 4:8 will not lead to a change of ball possession. It will only lead to the interruption of the game to order the player to correct the mistake and restart with a throw for the team which was in possession of the ball.
The organizers have the right to allow technical equipment in the substitution area. The equipment has to be used in a fair manner, and it does not include equipment for communication with a disqualified official or player.
All types and sizes of face masks and helmets are forbidden. Not only full masks but also masks to cover parts of the face are forbidden. As far as knee protections are concerned, it is not permitted to wear metallic parts. The plastic objects must be entirely padded. As far as ankle joint protections are concerned, all hard parts made of metal or plastic must be covered. Elbow protection is allowed only if made of soft material.
Federations and referees are not allowed to grant any exceptions. However, if a responsible team official addresses a delegate or a referee in case of doubt, they will make a decision on the basis of the regulations of Rule 4:9.
It is permitted to use glue. It is permitted to deposit glue on the shoes. This does not endanger the opponent’s health.
However, it is not permitted to deposit glue on the hands or the wrist. This endangers the opponents’ health, as glue might come into their eyes or their face. According to Rule 4:9 this practice is not allowed.
In cases where several players of the same team have been injured e.g. due to a collision, the referees or the delegate may give permission for additional eligible persons to enter the court in order to assist those injured players, with a maximum of two persons per injured player. Moreover the referees and the delegate monitor paramedics who may enter the court.
The goalkeeper is hit by a ball in play and is incapable of acting. Generally in these cases the protection of the goalkeeper must be given priority. In terms of restarting the game different situations are possible:
a) The ball passes the side line, the outer goal line, or is lying or rolling inside the goal area. Correct application of Rules: Immediate interruption of play, throw-in or goalkeeper throw in relation to the above cases, should be implemented to restart the game.
b) The referees interrupted the game before the ball passed the side line or the outer goal line or before the ball was lying or rolling inside the goal-area. Correct application of Rules: Restarting the game with the throw that corresponds to the situation.
c) The ball is in the air over the goal area. Correct application of Rules: Wait one or two seconds until one team gains possession of the ball, interrupt the game, restart the game with a free throw for the team in possession of the ball.
d) The referee whistles in a moment when the ball is still in the air. Correct application of Rules: Restart the game with a free throw for the team that last has been in possession of the ball.
e) The ball bounces from the goalkeeper incapable of acting back to an attacking player. Correct application of Rules: Interrupt the game immediately; restart the game with a free throw for the team in possession of the ball.
Comments:
In such cases a 7m throw is never possible. The referees interrupted the game deliberately for the protection of the goalkeeper. Therefore it is not a question of an ‘unwarranted whistle’ according to Rule 14:1b.
In compliance with Rule 7:3c,d putting down your foot for the first time after receiving the ball during a jump is not considered as a step (zero contact). However, ‘ball reception’ means receiving a pass.
Dribbling and catching the ball in the air during a jump is not considered as ‘ball reception’ according to the rule. Putting down your foot after dribbling has started is therefore without exception considered as a step.
See Training Support Passive Play
This applies when the goalkeeper comes from within the goal area or is in a similar position outside the goal area and causes a frontal collision with an opponent. It does not apply when:
a) the goalkeeper runs in the same direction as an opponent, for example, after re-entering the court from the substitution area.
b) the attacker runs after the ball, and the ball is between the attacker and the goalkeeper.
In such situations, the referees take a decision based on their observations of facts.
In cases where additional players or officials intervene, the decision on punishment and continuation of play are subject to the following criteria:
• player or official
• destroying a clear chance of scoring
Due to the named criteria the following situations could occur:
a) During a clear chance of scoring an additional player who has not been involved in a substitution process is present on the court. Correct application of Rules: 7m throw, disqualification to be reported in writing
b) Incorrect substitution: The timekeeper/delegate whistles during a clear chance of scoring. Correct application of Rules: 7m throw, 2min suspension.
c) During a clear chance of scoring a team official enters the court. Correct application of Rules: 7m throw, disqualification to be reported in writing.
d) As under c), but no clear chance of scoring. Correct application of Rules: free throw, progressive punishment.
The criteria for this highest level of punishment are defined in Rules 8:6 (for illegal behavior) and 8:10 (for unsportsmanlike behavior); see also Rule 8:3 section 2.
As the consequences of a punishment according to rule 8:6 or 8:10, during the game, do not differ from the penalty according to rules 8:5 and 8:9 (disqualification not to be reported in writing) the IHF added the following supplementary provision to both rules:
“... they must submit a written report after the game, so that the responsible authorities are in a position to take a decision about further measures.”
This supplementary provision builds the principle for the responsible authority to decide about the intended further measures. Not at all the wording of the rule “... are in position” may be interpreted as a discretion of the responsible authority, if further measures are taken. This would mean a change of fact-finding of the referees. Any enhancement of the disqualification punishment should not be reported in writing as intended by the IHF, and therefore is no longer necessary.
The following criteria assist in distinguishing between Rule 8:5 and Rule 8:6:
a) What defines ‘particularly reckless’?
• assaults and assault-similar actions
• ruthless or irresponsible actions without any sense of proper behaviour
• unrestrained hitting
• malevolent actions
b) What defines ‘particularly dangerous’?
• actions against an unprotected opponent
• extremely risky and serious actions endangering the opponent’s health
c) What defines ‘premeditated action’?
• intentional and deliberately committed malicious action
• willful action against the body of the opponent just to destroy the opponent’s action
d) What defines ‘malicious action’?
• sneaky and hidden action against the unprepared opponent
e) What defines ‘without any relation to the game situation’?
• actions committed far away from the player in possession of the ball
• actions without any relation to game tactics
If a team is playing without a goalkeeper and loses the ball, a court player of this team who is entering the team’s own goal area to gain an advantage is to be punished progressively.
Spitting at someone is considered an assault-similar action and must be punished in accordance with 8:10a (disqualification to be reported in writing). Differentiation between ‘successful spitting’ (punishment according to Rule 8:10) and ‘unsuccessful spitting’ (attempt, punishment according to Rule 8:9), which was previously introduced, remains unchanged.
The last 30 seconds of the game occur during regular playing time (end of 2nd half) as well as at the end of the second half during both overtime periods. The start of the last 30 seconds of the game begins when the clock indicates 59 minutes 30 seconds (or 69:30, 79:30) or 0 minutes 30 seconds.
“Not respecting the distance” leads to a disqualification + 7m throw, if a throw during the last 30 seconds of the game (!) cannot be executed.
The Rule is applicable if the infraction is committed during the last 30 seconds of the game or at the same time as the final signal (see Rule 2:4, 1st paragraph). In this case, the referees will make a decision on the basis of their observations of facts (Rule 17:11).
If the game is interrupted during the last 30 seconds due to an interference that is not directly related to the preparation or the execution of a throw (for example faulty substitution, unsportsmanlike conduct in the substitution area), Rule 8:10c is to be applied.
If the throw, for example, is executed but blocked by a player standing too close and actively destroying the result of the throw or disturbing the thrower during the execution, Rule 8:10c must also be applied.
If a player is standing less than three meters from the thrower but does not actively interfere with the execution, there will be no punishment. If the player standing too close uses this position to block the shot or intercept the pass from the thrower, Rule 8:10c also applies.
In case of a disqualification of a defending player according to Rules 8:5 and 8:6 during the last 30 seconds of the game, only infractions according to Rule 8:6 Comment lead to a disqualification to be reported in writing + 7m throw. Infractions of a defending player according to Rule 8:5 during the last 30 seconds of the game lead to a disqualification not to be reported in writing + 7m throw.
The referees interrupt the game and award a 7m at the latest when the player receiving a pass does not score a goal or continues the game by making another pass.
Rule 8:10d is applicable if the infraction is committed during the playing time or at the same time as the final signal (see Rule 2:4, 1st paragraph). In this case, the referees will make a decision on the basis of their observations of facts (Rule 17:11).
A disqualification of the goalkeeper according to Rule 8:5 Comment (Leaving the goal area) leads to a 7m throw during the last 30 seconds of the game if the conditions according to Rule 8:5, last paragraph, are fulfilled or an infraction is committed according to Rule 8:6.
When a goal/no-goal decision is required after the use of the video replay technology, there will be an extended deadline for disallowing a goal, which under Rule 9:2 is only until the subsequent throw-off has been taken, extending this limitation until the next change of ball possession.
A throw-in is executed in the direction of the playing court as direct throw passing the side line.
The definition of a clear chance of scoring in situations described in Clarification No. 6c when there is a clear and unimpeded opportunity to throw the ball into the empty goal requires that the player has possession of the ball and clearly attempts to shoot directly at the empty goal. This definition of a clear chance of scoring applies regardless of the type of violation and whether the ball is in or out of play, and any throw is to be executed from a correct position of the thrower and teammates.
Rule 15:7, 3rd paragraph and Rule 15:8 include examples of possible faults when executing a throw. Dribbling and putting the ball down on the floor (before taking it up again) is an infraction, as well as having the ball in contact with the floor when executing a throw (exception: goalkeeper throw).
In this case, faults are also to be treated according to the regulations of Rule 15:7 and 15:8 (correction or punishment).
Disqualified players and officials must leave the court and the substitution area immediately and must not have any contact with their team afterwards.
In cases where the referees recognize another infraction committed by a disqualified player or official, after restarting the game, must be reported in writing.
It is not possible, however, to extend further punishments in the game against the player or official concerned, and therefore, their behavior must not lead to a reduction in the number of players on the court. This is also valid in the event that a disqualified player enters the court.
If a player, after receiving a disqualification, is guilty of extremely unsportsmanlike conduct due to Rule 8:10a, the player is punished with an additional disqualification with a written report, and the team is reduced by one player for 4 minutes.
Rule 17:12 is also to be applied if spectators are behaving in a way to endanger players, for example by using a laser pointer or throwing different type of objects. In this case, the following measures are to be taken:
• if necessary, the game is suspended immediately and is not continued;
• the spectators are asked to stop disturbing the game;
• if necessary, spectators are removed from the corresponding stands and the game is only re-started when all spectators concerned have left the hall;
• the home team is asked to take additional safety measures;
• written report.
If the game has already been suspended when detecting the irregularity, Rule 13:3 (by analogy) is applicable.
If the game is suspended at the time of a clear chance of scoring, Rule 14:1c is applicable.
In all the other cases, a free throw has to be awarded to the team having been in possession of the ball from the spot where the ball was when play was interrupted.
| Helmet | Not Allowed | All kinds of helmets |
| Face Mask | Not Allowed | also masks covering parts of the face |
| Nose Protection | Allowed | Tape, soft material |
| Headband | Allowed | Elastic material |
| Head Scarf | Allowed | Elastic material |
| Captains' Armlet | Allowed | On upper arm, about 5 cm wide, one single color |
| Elbow Protection | Allowed | Soft material, thin, short |
| Wrist Protection | Allowed | Soft material, thin, short |
| Finger Band | Not Allowed | |
| Gloves | Not Allowed | |
| Knee Protection | Allowed | Soft material, no metal |
| Ankle Joint Protection | Allowed | hard parts covered |
| T-shirt for Court Player acting as Goalkeeper | Allowed | Identical to goalkeeper shirt, holes for front and back number, covered with transparent material |
| Long-sleeved Undershirt | Allowed | same colour as main colour of the shirt, thin material |
| Short Undershorts | Allowed | Same colour as pants, thin material |
| Long Undershorts | Not Allowed | |
| Long Pants | Not Allowed | Exception: Goalkeeper |
| Socks | Same color and length | |
| Clothing of Officials | Standardized, dressed in sportswear or civilian clothing; uniform colour, different from shirt colour of the court players of the opposing team |
